NRR:中南大学湘雅医院黄长盛教授团队探索了胶质淋巴系统和中枢神经炎症的复杂关系
撰文:邹凯璐,邓晴薇,张泓,黄长盛
近年来,越来越多的证据表明中枢神经系统存在定向的液体运输途径:胶质淋巴系统(glymphatic system)。Iliff等[1]于2012年首次提出胶质淋巴系统这一概念,并发现其在清除大脑代谢废物方面发挥关键的作用。胶质淋巴系统可帮助脑脊液沿穿透动脉的血管周围空间流入大脑深处,表达在星形胶质细胞终足的水通道蛋白4以促进脑脊液和间质液的混合和溶质的清除,然后间质液沿着引流静脉的血管周围空间离开大脑(图1)。胶质淋巴系统实现了脑脊液在整个大脑的往复流动,并最终通过脑膜淋巴管引流至颈部淋巴结等流出道离开大脑。作为大脑的类淋巴系统,胶质淋巴系统同样具有经典淋巴系统的运输、清除和免疫功能,其发现纠正了早期关于中枢神经系统的神经免疫学理论,并为完善神经炎症相关学说提供了新的可能。目前的一系列研究显示,在疾病背景下,中枢神经系统会出现神经炎症和胶质淋巴系统功能受损[2, 3]。但仍缺乏相关研究深入阐释二者之间的复杂关系以及它们是如何相互作用并促进中枢神经系统的功能障碍。
#br#
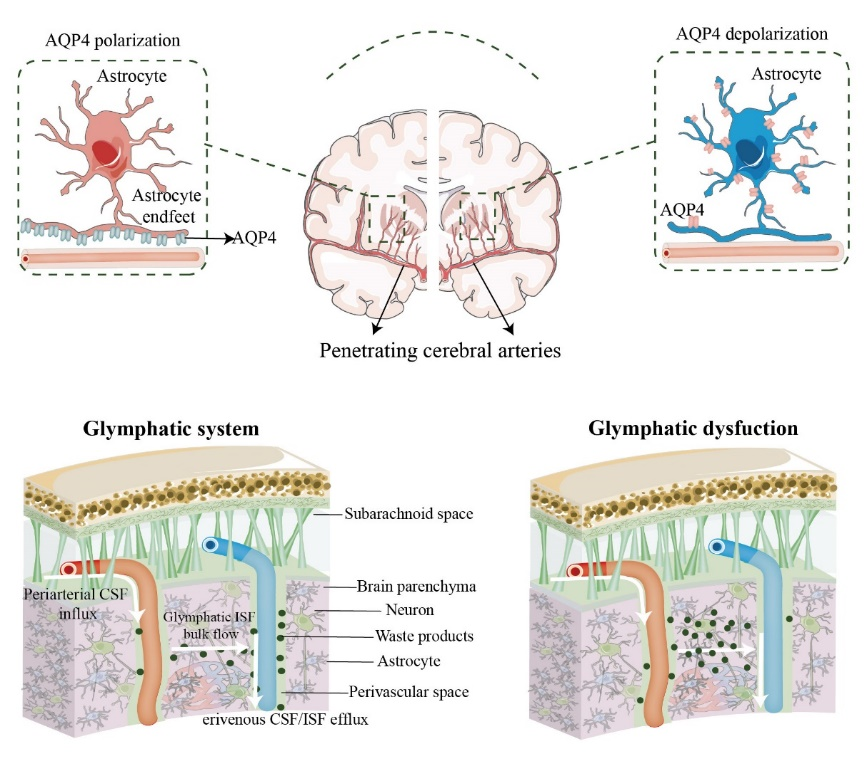
图1胶质淋巴系统模式(图源:Zou et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
最近中国中南大学黄长盛团队在《中国神经再生研究(英文版)》(Neural Regeneration Research)上发表了题为“Glymphatic system: a gateway for neuroinflammation”的综述,其总结了胶质淋巴系统功能障碍与神经炎症的关系,并综述了胶质淋巴系统无论是在中枢起源还是外周起源的疾病背景下均会出现功能受损。在此基础上,提出在系统性疾病中,外周炎症传递到大脑导致胶质淋巴障碍,从而引起中枢神经系统功能障碍和神经退行性病变这一假说。此外,胶质淋巴功能障碍可能是神经炎症慢性化的机制之一。这为探索胶质淋巴系统和神经炎症的复杂关系提供了新的视角,并为缓解神经炎症和中枢神经系统病变的治疗计划提供新的见解。#br#
血管周围空间在中枢神经系统炎症中发生改变,包括免疫细胞浸润、炎症因子聚集、以及血管周围空间体积和数量的增加。此外,中枢神经系统损伤后的继发性炎症信号,如环氧合酶1阳性细胞[4]、内皮单核细胞激活多肽II[5]、含铁血黄素[6]等在血管周围空间积聚和传播。水通道蛋白4对神经炎症则具有双重作用。一些研究认为,水通道蛋白4缺乏可以缓解神经炎症,起到神经保护的作用[7, 8]。而另一些研究认为,水通道蛋白4缺乏会增强神经炎症并加剧慢性神经损伤[9-11]。总之,不同的疾病模型和水通道蛋白4在星形胶质细胞的细胞定位均会对水通道蛋白4发挥的功能产生影响。因此,有必要对水通道蛋白4在胶质淋巴系统和神经炎症中的作用进行全面的研究。以上结果说明,胶质淋巴系统的两个关键结构——血管周围空间和水通道蛋白4均与神经炎症存在密切联系。#br#
目前的研究已在许多中枢神经系统疾病和系统性疾病中发现胶质淋巴系统的功能障碍[1, 12-15]。 胶质淋巴功能紊乱导致大脑中毒性废物的堆积,这是中枢神经病变加重的机制之一。此外,胶质淋巴系统实现了中枢神经系统和外周免疫系统之间的连接。脑脊液-间质液的混合液从脑膜淋巴管和颈部淋巴结顺利引流并释放免疫细胞和自身抗原,从而激活外周免疫系统[16]。既往的学说认为外周炎症可以通过神经、体液、免疫细胞三条途径传递到中枢并引起神经炎症。但外周损伤产生的神经炎症可能会长期存在并难以缓解,呈现慢性化进程[17],目前的研究对这一过程的解释仍不完善。黄长盛等认为外周炎症可能传播到大脑后损伤胶质淋巴系统,而胶质淋巴障碍正是导致神经炎症慢性化和神经退行性变的原因(图2)。需要强调的是,并不是任何程度的炎症都可以造成这一后果,只有较严重的炎症才能打击到胶质淋巴系统并造成大脑的不良结局。
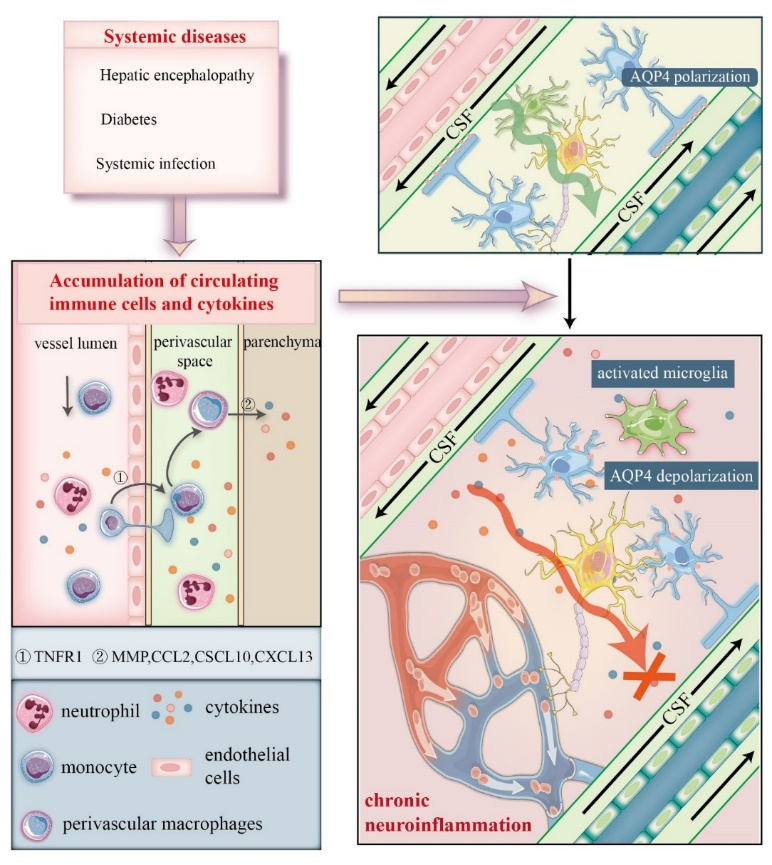
图2胶质淋巴功能障碍是外周炎症传到中枢并导致中枢炎症慢性化的一种机制(图源:Zou et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
无论是中枢性损伤还是外周性损伤,都能导致外周的炎症信号招募到中枢神经系统。除了脑膜淋巴管、吻侧迁移途径、筛板和鼻黏膜、受损的血脑屏障等,胶质淋巴系统也可能是这种外周和中枢的免疫交流“门户”之一。事实上,已经有动物实验表明,反复的脂多糖注射诱导的系统性炎症不仅显著降低脑脊液流量,而且会导致胶质淋巴系统的功能障碍[18]。在这一过程中,表达在血管内皮细胞上的肿瘤坏死因子受体1对外周炎症细胞到达血管周围空间至关重要。此外,循环中的细胞因子如白细胞介素1和肿瘤坏死因子α可以通过血管内皮细胞释放到另一侧,从而进入血管周围空间。基质金属蛋白酶和趋化因子通过控制趋化梯度帮助免疫细胞实现从血管周围空间到脑实质的跨越。以上证据都支持了黄长盛等的假说,作为一种新的病理机制,胶质淋巴系统架起了外周炎症和中枢神经系统功能障碍的“桥梁”。
胶质淋巴功能障碍和神经炎症在许多疾病过程中同时存在,因此黄长盛等探索了胶质淋巴系统如何帮助神经炎症加剧中枢神经系统症状。根据目前提供的证据来看,神经炎症和胶质淋巴功能障碍会相互影响,相互加重,从而形成恶性循环(图3)。一方面,脑脊液流量不足或胶质淋巴系统功能障碍会损伤大脑清除炎症介质的能力,从而导致促炎细胞因子和趋化因子的积聚,最终恶化炎症[2, 3]。另一方面,炎症信号会导致胶质淋巴功能受损。中性粒细胞释放的细胞外陷阱能够干扰胶质淋巴系统的液体转运,最终导致脑脊液的积聚和弥漫性脑肿胀[19]。活动性炎症可以扩大血管周围空间,这种扩张的血管周围空间可能是胶质淋巴系统液体输送停滞的主要因素[15, 20]。此外,异物诱导的局部炎症会导致周围脑膜淋巴管的增殖和胶质淋巴系统内流的急剧增加[21]。
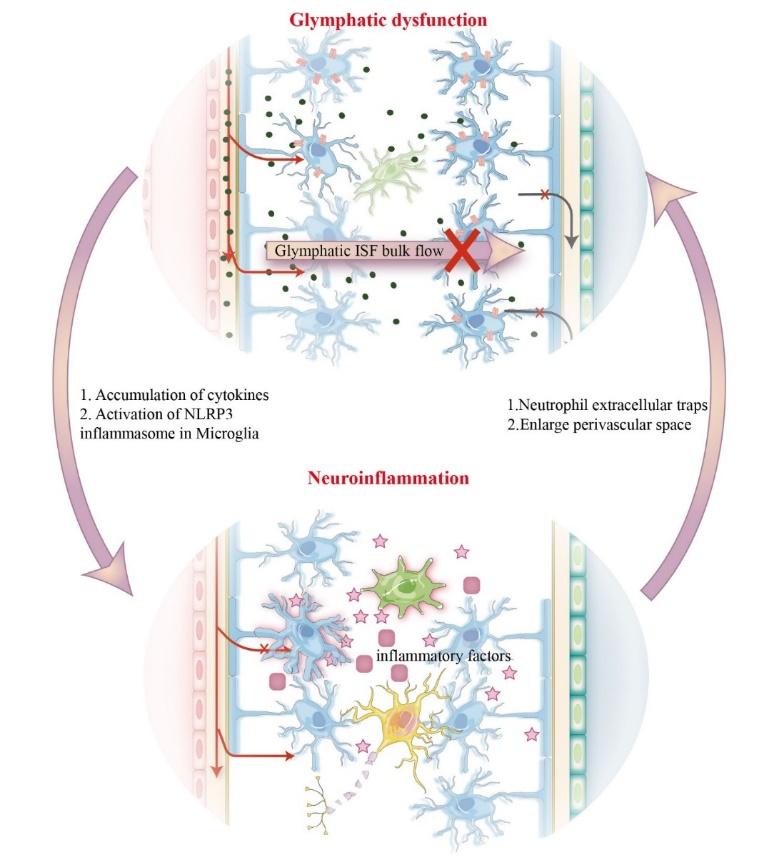
图3胶质淋巴功能障碍和神经炎症的恶性循环(图源:Zou et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
黄长盛等在这篇文章中阐释了胶质淋巴系统功能障碍与神经炎症之间的复杂联系,并为他们的假说提供了证据支持。但目前仍然缺乏全面的、系统的研究解释胶质淋巴系统参与外周和中枢神经系统免疫通讯的具体机制,需要进一步的研究验证胶质淋巴系统和神经炎症之间的确切互作关系。既往的研究证实了一些缓解神经炎症的策略,如食用多不饱和脂肪酸、β-羟基丁酸等[22, 23],可以改善胶质淋巴的功能。此外,目前也有一些治疗策略如电针、光生物疗法、地高辛等可以直接改善胶质淋巴系统的功能。这提示未来的研究可以将胶质淋巴系统作为突破点,为中枢神经系统疾病或系统性疾病的治疗提供新的思路。
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.391312
参考文献
[1] Iliff JJ, Wang M, Liao Y, et al. A paravascular pathway facilitates CSF flow through the brain parenchyma and the clearance of interstitial solutes, including amyloid β. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4(147):147ra111.
[2] Da Mesquita S, Herz J, Wall M, et al. Aging-associated deficit in CCR7 is linked to worsened glymphatic function, cognition, neuroinflammation, and β-amyloid pathology. Sci Adv. 2021;7(21):eabe4601.
[3] Liu X, Wu G, Tang N, et al. Glymphatic drainage blocking aggravates brain edema, neuroinflammation via modulating TNF-α, IL-10, and AQP4 after intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021;15:784154.
[4] Schwab JM, Nguyen TD, Postler E, et al. Selective accumulation of cyclooxygenase-1-expressing microglial cells/macrophages in lesions of human focal cerebral ischemia. Acta Neuropathol. 2000;99(6):609-614.
[5] Mueller CA, Schluesener HJ, Conrad S, et al. Spinal cord injury induces lesional expression of the proinflammatory and antiangiogenic cytokine EMAP II. J Neurotrauma. 2003;20(10):1007-1015.
[6] Schrag M, Mcauley G, Pomakian J, et al. Correlation of hypointensities in susceptibility-weighted images to tissue histology in dementia patients with cerebral amyloid angiopathy: a postmortem MRI study. Acta Neuropathol. 2010;119(3):291-302.
[7] Liu X, Xie Y, Wan X, et al. Protective effects of aquaporin-4 deficiency on longer-term neurological outcomes in a mouse model. Neurochem Res. 2021;46(6):1380-1389.
[8] Zhao F, Deng J, Xu X, et al. Aquaporin-4 deletion ameliorates hypoglycemia-induced BBB permeability by inhibiting inflammatory responses. J Neuroinflammation. 2018;15(1):157.
[9] Sun H, Liang R, Yang B, et al. Aquaporin-4 mediates communication between astrocyte and microglia: Implications of neuroinflammation in experimental Parkinson's disease. Neuroscience. 2016;317:65-75.
[10] Shi WZ, Qi LL, Fang SH, et al. Aggravated chronic brain injury after focal cerebral ischemia in aquaporin-4-deficient mice. Neurosci Lett. 2012;520(1):121-125.
[11] Shi WZ, Zhao CZ, Zhao B, et al. Aquaporin-4 deficiency attenuates acute lesions but aggravates delayed lesions and microgliosis after cryoinjury to mouse brain. Neurosci Bull. 2012;28(1):61-68.
[12] Golanov EV, Bovshik EI, Wong KK, et al. Subarachnoid hemorrhage - Induced block of cerebrospinal fluid flow: Role of brain coagulation factor III (tissue factor). J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2018;38(5):793-808.
[13] Iliff JJ, Chen MJ, Plog BA, et al. Impairment of glymphatic pathway function promotes tau pathology after traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci. 2014;34(49):16180-16193.
[14] Hadjihambi A, Harrison IF, Costas-Rodríguez M, et al. Impaired brain glymphatic flow in experimental hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol. 2019;70(1):40-49.
[15] Jiang Q, Zhang L, Ding G, et al. Impairment of the glymphatic system after diabetes. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017;37(4):1326-1337.
[16] Louveau A, Herz J, Alme MN, et al. CNS lymphatic drainage and neuroinflammation are regulated by meningeal lymphatic vasculature. Nat Neurosci. 2018;21(10):1380-1391.
[17] Ren WJ, Liu Y, Zhou LJ, et al. Peripheral nerve injury leads to working memory deficits and dysfunction of the hippocampus by upregulation of TNF-α in rodents. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011;36(5):979-992.
[18] Manouchehrian O, Ramos M, Bachiller S, et al. Acute systemic LPS-exposure impairs perivascular CSF distribution in mice. J Neuroinflammation. 2021;18(1):34.
[19] Pavan C, A LRX, Ramos M, et al. DNase treatment prevents cerebrospinal fluid block in early experimental pneumococcal meningitis. Ann Neurol. 2021;90(4):653-669.
[20] Wuerfel J, Haertle M, Waiczies H, et al. Perivascular spaces--MRI marker of inflammatory activity in the brain? Brain. 2008;131(Pt 9):2332-2340.
[21] Hauglund NL, Kusk P, Kornum BR, et al. Meningeal lymphangiogenesis and enhanced glymphatic activity in mice with chronically implanted EEG electrodes. J Neurosci. 2020;40(11):2371-2380.
[22] Liu X, Hao J, Yao E, et al. Polyunsaturated fatty acid supplement alleviates depression-incident cognitive dysfunction by protecting the cerebrovascular and glymphatic systems. Brain Behav Immun. 2020;89:357-370.
[23] Wang FX, Xu CL, Su C, et al. β-Hydroxybutyrate attenuates painful diabetic neuropathy via restoration of the aquaporin-4 polarity in the spinal glymphatic system. Front Neurosci. 2022;16:926128.
邹凯璐为论文第一作者。

通讯作者:黄长盛教授是中南大学湘雅医院麻醉手术部博士研究生导师,长期致力于急性和慢性疼痛的临床与基础研究,近年来主持国家级和省部级项目7项,以第一或通讯作者在Redox Biology、Glia、Brain Behav Immun、Br J Anaesth等国际著名期刊发表系列研究论文。



