NRR:重庆医科大学李英博团队揭示褪黑素对Ctnnd2缺失诱导的前额皮质突触发育异常的改善作用
撰文:王路义,李英博
孤独症谱系障碍是一组与1100多种基因相关的神经发育障碍疾病[1],其中一些基因是突触和树突棘结构与功能的关键调节因子[2]。研究表明,孤独症谱系障碍患者和小鼠模型的大脑皮质中存在树突棘异常[3-5]。Delta catenin 2(CTNND2)是一种新的孤独症基因[6],负责编码δ-catenin蛋白,后者是一种涉及黏附和树突分支的神经元特异性蛋白[7, 8]。在之前的实验中,作者建立了Ctnnd2基因敲除小鼠模型,并证明其可表现出孤独症谱系障碍样行为和海马树突棘密度降低[9]。虽然孤独症谱系障碍的发病机制在很大程度上是未知的,但各种动物模型表明孤独症谱系障碍是中枢神经系统兴奋/抑制失衡的结果[10]。谷氨酸脱羧酶67和谷氨酸脱羧酶65均可催化谷氨酸脱羧形成抑制性神经递质γ-氨基丁酸,参与维持兴奋/抑制平衡。谷氨酸脱羧酶67分布在细胞内,负责90%以上的γ-氨基丁酸合成,而谷氨酸脱羧酶65特异地定位于突触末端[11-13]。γ-氨基丁酸的释放导致突触后A型γ-氨基丁酸受体的激活,触发快速抑制电流。该受体的组成包括α5亚基,研究表明,α5亚基在γ-氨基丁酸能突触/突触外位点的平衡分布对树突生长和树突棘成熟至关重要[14]。此外,过度激活A型γ-氨基丁酸受体可产生异常的树突分支和树突棘密度[15]。褪黑素可改善孤独症谱系障碍患者的社会行为缺陷[16],并在脑损伤模型中发挥神经保护作用[17]。褪黑素还可通过增加突触前蛋白的水平,促进突触形成[18]。此外,长期和短期褪黑素治疗均可促进树突棘发育和神经元形成[19-21]。然而,目前尚不清楚Ctnnd2基因敲除引起的突触发育受损应如何干预,研究者旨在探索褪黑素对Ctnnd2缺失诱导的前额皮质突触发育异常的改善作用。
来自中国重庆医科大学李英博团队在《中国神经再生研究(英文版)》(Neural Regeneration Research)上发表了题为“Melatonin improves synapse development by PI3K/Akt signaling in a mouse model of autism spectrum disorder”的研究,发现Ctnnd2基因缺失可导致C57BL/6J小鼠社交行为障碍和树突棘丢失。口服褪黑素可减轻Ctnnd2基因敲除小鼠社交行为异常和树突棘损伤。此外,褪黑素还可通过结合其受体,激活磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶/Akt信号通路,改善γ-氨基丁酸能神经元的突触功能,这可能与褪黑素改善Ctnnd2基因敲除小鼠树突棘的异常有关。这一研究为Ctnnd2缺失引起的神经发育障碍提供了潜在的治疗靶点。
大多数关于褪黑素神经保护作用的研究都集中在对神经元的病理改善作用上。褪黑素可保护皮质和海马神经元树突和树突棘的完整性,从而逆转脑损伤和神经功能缺陷[21-24]。此外,褪黑素也对孤独症谱系障碍样行为的治疗作用可能与突触发育和可塑性改善有关[16, 25, 26]。因此,李英博等观察到Ctnnd2基因敲除小鼠表现出异常的社交行为和树突棘后,通过口服褪黑素进行干预。连续28d褪黑素(5、10和50 mg/kg)治疗可减轻基因敲除小鼠的社交行为障碍和树突棘丢失,其中10 mg/kg褪黑素效果最佳(图1和2)。
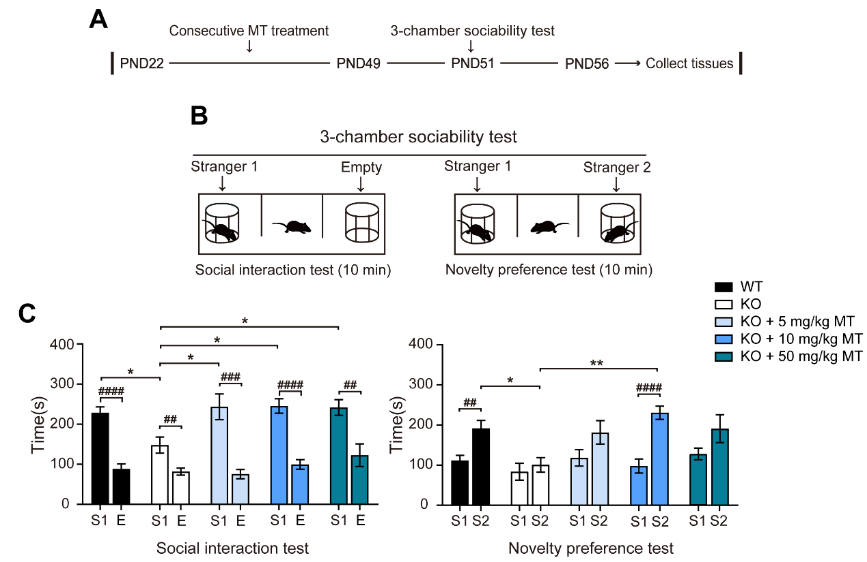
图1 褪黑素可减轻Ctnnd2基因敲除小鼠的社交行为缺陷(图源:Wang et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
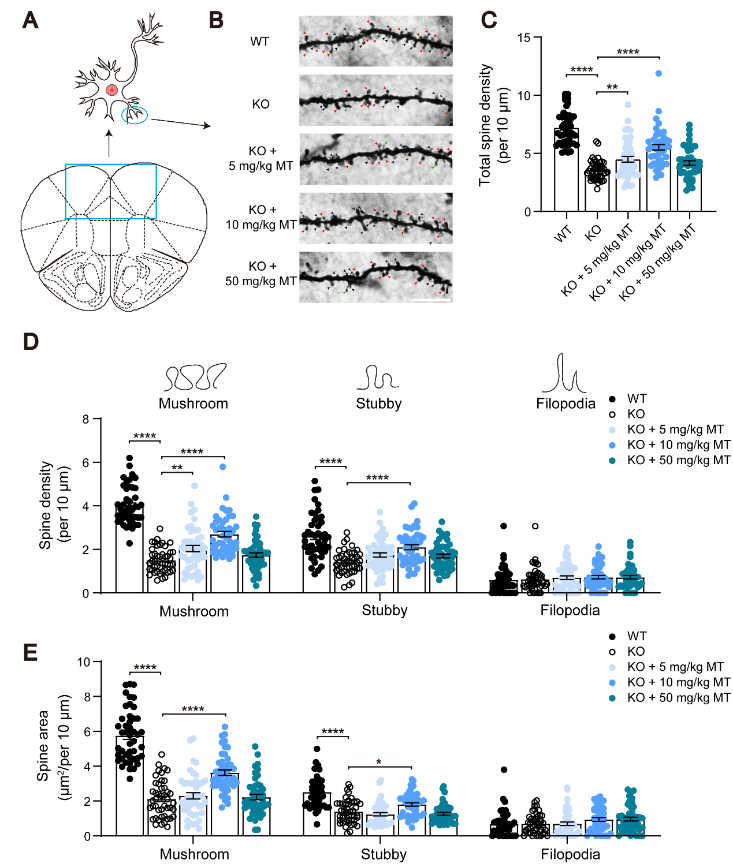
图2 褪黑素可改善Ctnnd2 敲除小鼠树突棘的异常(图源:Wang et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
兴奋/抑制比值升高是孤独症谱系障碍的发病机制理论假说之一[27],通过激活γ-氨基丁酸能信号纠正兴奋/抑制失衡可减轻小鼠孤独症谱系障碍的严重程度[28]。研究显示,基因敲除小鼠全脑谷氨酸脱羧酶67的表达减少,特别是前额皮质,而谷氨酸脱羧酶65的表达无明显变化(图3),这表明γ-氨基丁酸水平降低,兴奋/抑制平衡受损。松果体切除动物的γ-氨基丁酸水平下降,可通过后续褪黑素治疗恢复[29]。动物研究也报道了褪黑素可以通过改变A型γ-氨基丁酸受体的效力来调节γ-氨基丁酸能信号传导[29, 30]。此外,使用A型γ-氨基丁酸受体亚基阳性变构调节剂可增加前额皮质的树突棘密度[31],这一发现与A型γ-氨基丁酸受体可调节树突棘密度,特别是蘑菇状树突棘密度的观点一致[15, 32]。以上结果表明,褪黑素可能通过调节γ-氨基丁酸能信号改善树突棘的丢失。然而,作者发现褪黑素并没有改善谷氨酸脱羧酶67的表达(图4A和B)。
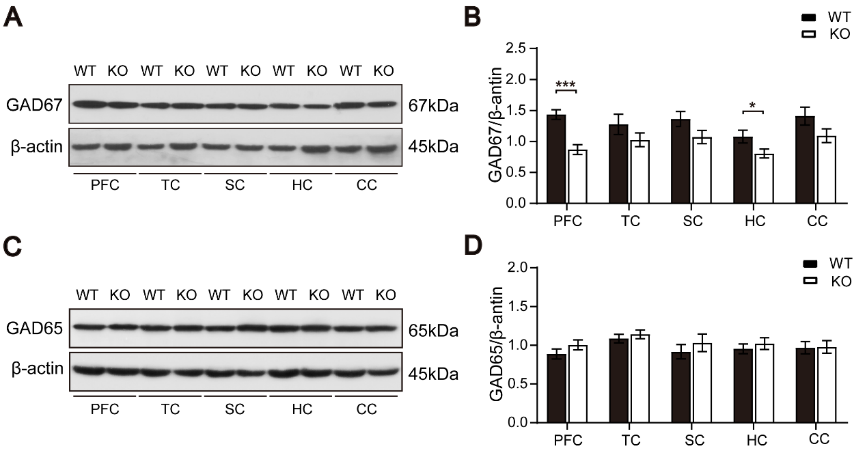
图3 野生型和Ctnnd2基因敲除小鼠全脑谷氨酸脱羧酶67和谷氨酸脱羧酶65的表达(图源:Wang et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
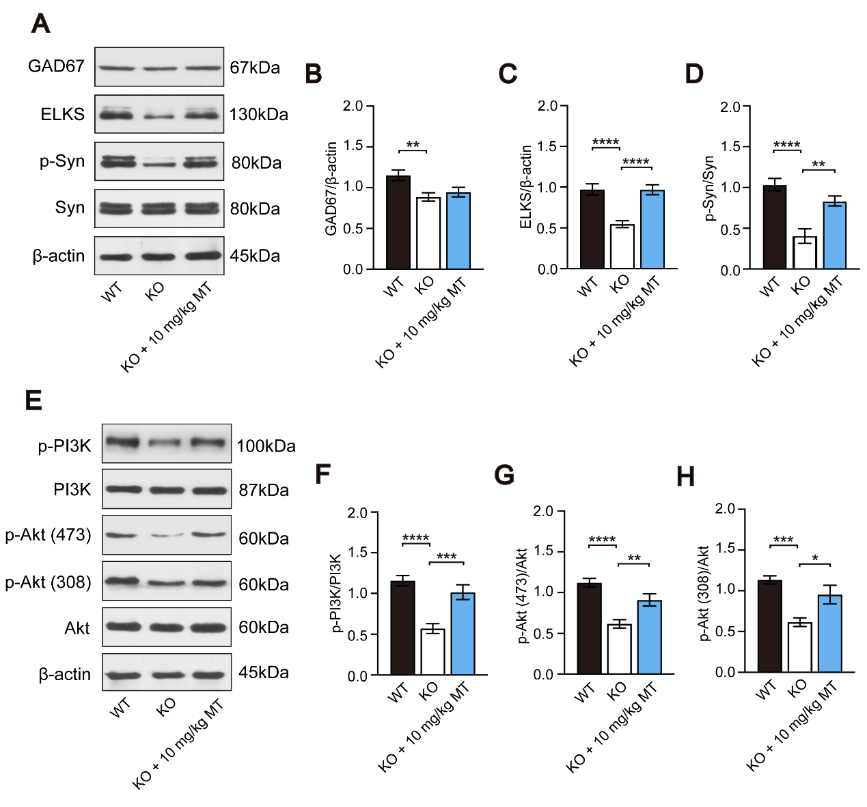
图4褪黑素促进Ctnnd2基因敲除小鼠突触相关蛋白的表达并激活磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶/Akt信号通路(图源:Wang et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
褪黑素激活磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶/Akt信号通路是预防各种神经系统疾病的重要机制[33]。该信号通路的激活可以诱导树突棘和突触形成[34],同样,长期或短期阻断磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶/Akt信号通路会影响神经元树突棘的形成和密度[35]。李英博等发现Ctnnd2基因缺失抑制了磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶/Akt信号通路,在连续28d的褪黑素处理后,该通路被激活(图4E-H),提示该信号通路可能参与了褪黑素对Ctnnd2基因敲除小鼠树突棘发育的影响。
ELKS是活性区相关结构中的一种蛋白质,与靠近突触前膜的囊泡对接。研究显示,ELKS基因敲除小鼠停靠的囊泡数量大幅减少[36, 37]。突触素(synapsin)是突触前末端突触囊泡动力学的重要调节因子;当突触素磷酸化时,突触囊泡被传递到易释放池和活性区。因此,突触素通过控制易释放池中突触囊泡的储存和动员来调节突触传递[38-40]。结果显示,Ctnnd2基因敲除导致ELKS和磷酸化突触素表达的明显降低,在连续28d的褪黑素治疗后,这种下降可以缓解(图4C和D),提示褪黑素可以恢复敲除小鼠的突触功能。
为进一步探讨褪黑素影响Ctnnd2基因敲除小鼠树突棘发育的相关分子机制,李英博等采用局部输注的方法。在前额皮质局部输注褪黑素后,敲除小鼠ELKS、磷酸化突触素、磷酸化磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶和磷酸化Akt(Ser473)的表达增加,局部输注渥曼青霉素(wortmannin)则可逆转褪黑素对磷酸化突触素和ELKS表达的影响。此外,在前额皮质局部输注褪黑素受体抑制剂luzindole和4p-p-Dot也能逆转褪黑素对ELKS、磷酸化突触素、磷酸化磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶和磷酸化Akt(Ser473)表达水平的影响(图5),提示褪黑素可以通过与褪黑素受体结合激活磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶/Akt信号通路来改善突触功能。
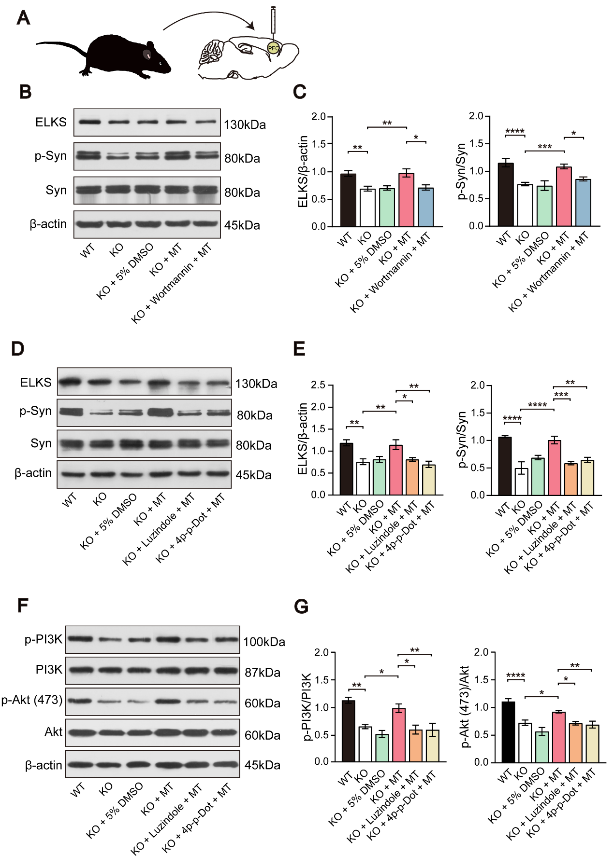
图5褪黑素与褪黑素受体结合,可激活磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶/Akt信号通路,改善Ctnnd2基因敲除小鼠突触功能(图源:Wang et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
褪黑素与褪黑素受体结合,在许多神经精神疾病中起着重要作用。即使在不产生褪黑素的情况下,C57BL/6J小鼠的神经元也能表达褪黑素受体[41, 42]。内源性褪黑素主要通过褪黑素受体1和褪黑素受体2介导。研究表明,海马中4p-p-Dot对褪黑素受体2的抑制可以防止癫痫的发作,并且比褪黑素受体拮抗剂luzindole更大程度地增加癫痫发作的潜伏期[43]。在本研究中,作者观察到γ-氨基丁酸能神经元表达褪黑素受体1和2(图6)。免疫荧光结果显示,敲除小鼠ELKS阳性和磷酸化突触素阳性的γ-氨基丁酸能神经元减少,局部输注褪黑素后,ELKS阳性和磷酸化突触素阳性的γ-氨基丁酸能神经元数量增加,但这些变化可以被wortmannin、luzindole和4p-p-Dot逆转(图7),提示褪黑素可以通过与褪黑素受体结合,激活磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶/Akt信号通路,改善Ctnnd2基因敲除小鼠γ-氨基丁酸能神经元的突触功能。
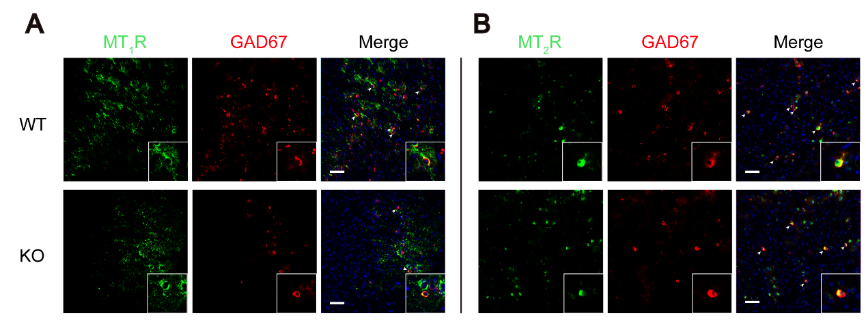
图6 Ctnnd2基因敲除小鼠的γ-氨基丁酸能神经元上同时表达褪黑素受体1和2(图源:Wang et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
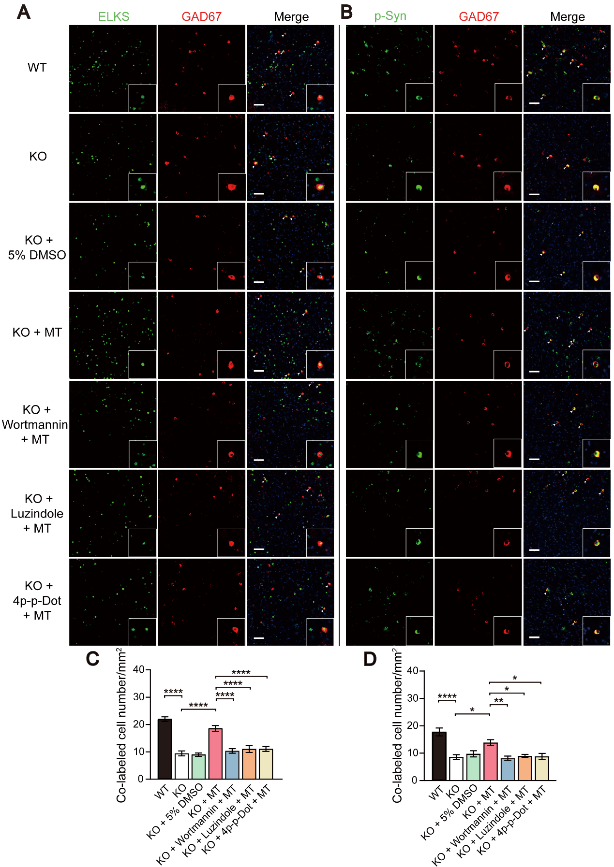
图7褪黑素通过与褪黑素受体结合,激活磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶/Akt信号通路,改善Ctnnd2基因敲除小鼠γ-氨基丁酸能神经元的突触功能(图源:Wang et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
综上所述,褪黑素可以在一定程度上改善Ctnnd2基因敲除小鼠的社交行为缺陷和树突棘异常。褪黑素还可以通过结合褪黑素受体,激活磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶/Akt信号通路,改善γ-氨基丁酸能神经元的突触功能,这可能与褪黑素改善Ctnnd2基因敲除小鼠的树突棘异常有关。这一研究首次揭示了褪黑素对Ctnnd2基因敲除小鼠发挥神经保护作用的潜在机制,为Ctnnd2缺失引起的神经发育障碍提供了可能的治疗靶点。但研究也存在局限性:首先,该研究只间接验证了γ-氨基丁酸能神经元的变化。未来的研究应该直接观察γ-氨基丁酸能神经元的改变,如递质传递。其次,未直接验证γ-氨基丁酸能信号与树突棘发育的关系。需要进一步实验证明γ-氨基丁酸能神经元调节树突棘发育。
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.387973
参考文献
[1] Vorstman JaS, Parr JR, Moreno-De-Luca D, et al. Autism genetics: opportunities and challenges for clinical translation. Nat Rev Genet. 2017;18(6):362-376.
[2] Zoghbi HY, Bear MF. Synaptic dysfunction in neurodevelopmental disorders associated with autism and intellectual disabilities. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012;4(3):a009886.
[3] Hutsler JJ, Zhang H. Increased dendritic spine densities on cortical projection neurons in autism spectrum disorders. Brain Res. 2010;1309:83-94.
[4] Cruz-Martín A, Crespo M, Portera-Cailliau C. Delayed stabilization of dendritic spines in fragile X mice. J Neurosci. 2010;30(23):7793-7803.
[5] Guo D, Peng Y, Wang L, et al. Autism-like social deficit generated by Dock4 deficiency is rescued by restoration of Rac1 activity and NMDA receptor function. Mol Psychiatry. 2021;26(5):1505-1519.
[6] Turner TN, Sharma K, Oh EC, et al. Loss of δ-catenin function in severe autism. Nature. 2015;520(7545):51-56.
[7] Lu Q, Paredes M, Medina M, et al. delta-catenin, an adhesive junction-associated protein which promotes cell scattering. J Cell Biol. 1999;144(3):519-532.
[8] Kim K, Sirota A, Chen Yh YH, et al. Dendrite-like process formation and cytoskeletal remodeling regulated by delta-catenin expression. Exp Cell Res. 2002;275(2):171-184.
[9] Wang X, Xu M, Xu Q, et al. Rictor is involved in Ctnnd2 deletion-induced impairment of spatial learning and memory but not autism-like behaviors. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2021;26(8):335-346.
[10] Rubenstein JL, Merzenich MM. Model of autism: increased ratio of excitation/inhibition in key neural systems. Genes Brain Behav. 2003;2(5):255-267.
[11] Soghomonian JJ, Martin DL. Two isoforms of glutamate decarboxylase: why? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1998;19(12):500-505.
[12] Asada H, Kawamura Y, Maruyama K, et al. Cleft palate and decreased brain gamma-aminobutyric acid in mice lacking the 67-kDa isoform of glutamic acid decarboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94(12):6496-6499.
[13] Tian N, Petersen C, Kash S, et al. The role of the synthetic enzyme GAD65 in the control of neuronal gamma-aminobutyric acid release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96(22):12911-12916.
[14] Brady ML, Jacob TC. Synaptic localization of α5 GABA (A) receptors via gephyrin interaction regulates dendritic outgrowth and spine maturation. Dev Neurobiol. 2015;75(11):1241-1251.
[15] Afroz S, Shen H, Smith SS. α4βδ GABA(A) receptors reduce dendritic spine density in CA1 hippocampus and impair relearning ability of adolescent female mice: effects of a GABA agonist and a stress steroid. Neuroscience. 2017;347:22-35.
[16] Tian Y, Yabuki Y, Moriguchi S, et al. Melatonin reverses the decreases in hippocampal protein serine/threonine kinases observed in an animal model of autism. J Pineal Res. 2014;56(1):1-11.
[17] Hossain MF, Uddin MS, Uddin GMS, et al. Melatonin in Alzheimer's disease: a latent endogenous regulator of neurogenesis to mitigate Alzheimer's neuropathology. Mol Neurobiol. 2019;56(12):8255-8276.
[18] Domínguez-Alonso A, Ramírez-Rodríguez G, Benítez-King G. Melatonin increases dendritogenesis in the hilus of hippocampal organotypic cultures. J Pineal Res. 2012;52(4):427-436.
[19] Ramirez-Rodriguez G, Ortíz-López L, Domínguez-Alonso A, et al. Chronic treatment with melatonin stimulates dendrite maturation and complexity in adult hippocampal neurogenesis of mice. J Pineal Res. 2011;50(1):29-37.
[20] González-Burgos I, Letechipía-Vallejo G, López-Loeza E, et al. Long-term study of dendritic spines from hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells, after neuroprotective melatonin treatment following global cerebral ischemia in rats. Neurosci Lett. 2007;423(2):162-166.
[21] Chen HY, Hung YC, Chen TY, et al. Melatonin improves presynaptic protein, SNAP-25, expression and dendritic spine density and enhances functional and electrophysiological recovery following transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J Pineal Res. 2009;47(3):260-270.
[22] Crupi R, Mazzon E, Marino A, et al. Melatonin treatment mimics the antidepressant action in chronic corticosterone-treated mice. J Pineal Res. 2010;49(2):123-129.
[23] Lin XJ, Liu R, Li C, et al. Melatonin ameliorates spatial memory and motor deficits via preserving the integrity of cortical and hippocampal dendritic spine morphology in mice with neurotrauma. Inflammopharmacology. 2020;28(6):1553-1566.
[24] Tang H, Ma M, Wu Y, et al. Activation of MT2 receptor ameliorates dendritic abnormalities in Alzheimer's disease via C/EBPα/miR-125b pathway. Aging Cell. 2019;18(2):e12902.
[25] Ebert DH, Greenberg ME. Activity-dependent neuronal signalling and autism spectrum disorder. Nature. 2013;493(7432):327-337.
[26] Takeuchi K, Gertner MJ, Zhou J, et al. Dysregulation of synaptic plasticity precedes appearance of morphological defects in a Pten conditional knockout mouse model of autism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(12):4738-4743.
[27] Goel A, Portera-Cailliau C. Autism in the Balance: Elevated E-I ratio as a homeostatic stabilization of synaptic drive. Neuron. 2019;101(4):543-545.
[28] Sun X, Wang L, Wei C, et al. Dysfunction of Trio GEF1 involves in excitatory/inhibitory imbalance and autism-like behaviors through regulation of interneuron migration. Mol Psychiatry. 2021;26(12):7621-7640.
[29] Wu FS, Yang YC, Tsai JJ. Melatonin potentiates the GABA(A) receptor-mediated current in cultured chick spinal cord neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1999;260(3):177-180.
[30] Cheng XP, Sun H, Ye ZY, et al. Melatonin modulates the GABAergic response in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. J Pharmacol Sci. 2012;119(2):177-185.
[31] Prevot TD, Sumitomo A, Tomoda T, et al. Reversal of age-related neuronal atrophy by α5-GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulation. Cereb Cortex. 2021;31(2):1395-1408.
[32] Heinen K, Baker RE, Spijker S, et al. Impaired dendritic spine maturation in GABAA receptor alpha1 subunit knock out mice. Neuroscience. 2003;122(3):699-705.
[33] Kilic U, Caglayan AB, Beker MC, et al. Particular phosphorylation of PI3K/Akt on Thr308 via PDK-1 and PTEN mediates melatonin's neuroprotective activity after focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Redox Biol. 2017;12:657-665.
[34] Lee CC, Huang CC, Hsu KS. Insulin promotes dendritic spine and synapse formation by the PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Rac1 signaling pathways. Neuropharmacology. 2011;61(4):867-879.
[35] Kumar V, Zhang MX, Swank MW, et al. Regulation of dendritic morphogenesis by Ras-PI3K-Akt-mTOR and Ras-MAPK signaling pathways. J Neurosci. 2005;25(49):11288-11299.
[36] Wang SSH, Held RG, Wong MY, et al. Fusion competent synaptic vesicles persist upon active zone disruption and loss of vesicle docking. Neuron. 2016;91(4):777-791.
[37] Acuna C, Liu X, Südhof TC. How to make an active zone: unexpected universal functional redundancy between RIMs and RIM-BPs. Neuron. 2016;91(4):792-807.
[38] Kim JH, Lee CH, Kim HG, et al. Decreased dopamine in striatum and difficult locomotor recovery from MPTP insult after exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic fields. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):1201.
[39] Shupliakov O, Haucke V, Pechstein A. How synapsin I may cluster synaptic vesicles. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011;22(4):393-399.
[40] Bykhovskaia M. Synapsin regulation of vesicle organization and functional pools. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011;22(4):387-392.
[41] Lin JJ, Lin Y, Zhao TZ, et al. Melatonin suppresses neuropathic pain via MT2-dependent and -independent pathways in dorsal root ganglia neurons of mice. Theranostics. 2017;7(7):2015-2032.
[42] Sharma R, Sahota P, Thakkar MM. Melatonin promotes sleep in mice by inhibiting orexin neurons in the perifornical lateral hypothalamus. J Pineal Res. 2018;65(2):e12498.
[43] Stewart LS, Leung LS. Hippocampal melatonin receptors modulate seizure threshold. Epilepsia. 2005;46(4):473-480.
第一作者:王路义,女,重庆医科大学基础医学院生理学硕士毕业。

通讯作者:李英博,男,医学博士,副教授,重庆医科大学人体机能实验室主任,主攻脑血管疾病和孤独症的研究。主持及参与国家自然科学基金等各级科研课题10余项,发表SCI、CSCD等论文20余篇。







