NRR:杭州师范大学、杭州市第一人民医院王莹团队总结小胶质细胞乳酸化与中枢神经系统疾病的互作
撰文:杨慧,岳娟清,王莹
小胶质细胞来源于卵黄囊内的红髓祖细胞,是中枢神经系统的常驻免疫细胞,约占脑细胞总数的10-15%,在维持中枢神经系统稳态、损伤反应和神经退行性疾病中发挥着重要的作用 ADDIN EN.CITE ADDIN EN.CITE.DATA [1, 2]。小胶质细胞的监测和清除功能随着年龄的增长而下降,且与多种神经退行性疾病的发展密切相关。乳酸化是近年来新发现的表观遗传修饰之一,也是乳酸发挥作用的重要途径,参与糖酵解相关功能、巨噬细胞极化、神经调节和血管生成,并参与多种疾病的发生发展 ADDIN EN.CITE ADDIN EN.CITE.DATA [3, 4]。小胶质细胞的乳酸代谢和稳态调节,组蛋白与非组蛋白的乳酸化等在各种疾病中发挥着重要作用。对小胶质细胞乳酸代谢和乳酸化修饰调控机制的深入了解将为疾病的治疗以及药物的开发提供更多选择。然而,目前关于小胶质细胞乳酸化修饰在中枢神经系统疾病中的研究仍缺乏全面的总结。
最近,来自中国杭州师范大学、杭州市第一人民医院王莹团队在《中国神经再生研究(英文版)》(Neural
Regeneration Research)上发表了题为“Microglia
lactylation in relation to central nervous system diseases”的综述,总结和讨论了小胶质细胞乳酸化的作用机制及其在中枢神经系统疾病中作用,其中包括阿尔茨海默症、缺氧缺血性脑病等。综述对小胶质细胞乳酸化代谢调控机制的深入了解将为中枢神经系统疾病的治疗提供更多选择。
神经胶质细胞在中枢神经系统中丰富,在大脑发育和体内平衡中起着关键作用。小胶质细胞作为中枢神经系统的先天免疫细胞,与巨噬细胞类似,参与炎症反应、稳态调节和中枢神经系统疾病的发生,同时与脑内其他细胞如星形胶质细胞和少突胶质细胞相互作用 ADDIN EN.CITE ADDIN EN.CITE.DATA [2]。随着年龄的增长和中枢神经系统疾病的进展,小胶质细胞的免疫监视功能逐渐丧失,小胶质细胞损伤可导致神经炎症和神经退行性病变。
乳酸是正常细胞缺氧时糖酵解的副产物,长期以来被认为是一种代谢废物。然而,近年来的研究逐渐揭示了乳酸的生物学功能。乳酸可以作为一种能量物质被运输到细胞中参与代谢。此外,乳酸可以通过其特异性受体G蛋白偶联受体81发出信号,作为信号分子介导细胞内或细胞间信号传导,并在调节先天免疫信号传导中发挥作用。乳酸在细胞之间穿梭,受浓度梯度、pH梯度和氧化还原状态的影响,并通过多种羟羧酸受体,包括单羧酸转运蛋白1、单羧酸转运蛋白2和单羧酸转运蛋白4转运到细胞中,以维持乳酸稳态 ADDIN EN.CITE ADDIN EN.CITE.DATA [5, 6]。在肿瘤研究中发现,乳酸还可以促进肿瘤血管生成,并协助肿瘤免疫逃逸 ADDIN EN.CITE ADDIN EN.CITE.DATA [7-9]。然而,这些生物学功能背后的分子机制仍有待探索。乳酸作为代谢过程中产生的一种小分子,不仅要承担代谢的主要工作,而且作为底物被共价修饰到组蛋白参与表观遗传调控。2019年,乳酸被发现作为底物可添加到组蛋白赖氨酸残基上参与转录后调控,即乳酸化修饰,开启了蛋白质乳酸化研究的新时代。乳酸化是乳酸发挥功能的重要途径,参与糖酵解相关的细胞功能、巨噬细胞极化、神经调节和血管生成等重要生命活动 ADDIN EN.CITE ADDIN EN.CITE.DATA [10],与肿瘤增殖、焦虑抑郁、缺氧缺血性疾病、无氧运动代谢等多种疾病也有密切联系 ADDIN EN.CITE ADDIN EN.CITE.DATA [11]。组蛋白乳酸化的增加也可以促进参与损伤修复过程的稳态基因的表达。乳酸化作为新兴研究热点受到广泛关注,乳酸化的发现为蛋白质的翻译后修饰和乳酸在疾病中的研究翻开了新篇章。
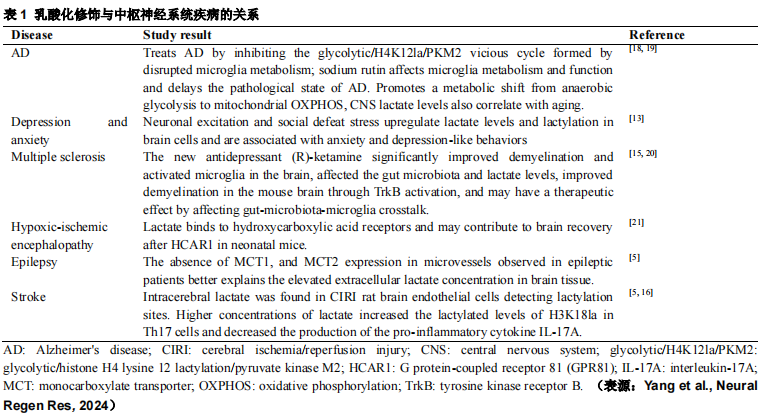
小胶质细胞作为中枢神经系统的免疫细胞,具有与巨噬细胞相似的功能。小胶质细胞可以通过适应和调节乳酸代谢、吞噬和炎症反应来影响大脑的生理和病理,达到治疗目的。小胶质细胞通过糖酵解和氧化磷酸化进行能量代谢。静息的小胶质细胞主要依靠糖酵解和氧化磷酸化产生ATP,而激活的小胶质细胞表现出从糖酵解和氧化磷酸化到糖酵解的代谢转换表型(图1)。这种代谢机制已在多种中枢神经系统疾病中被观察到。阿尔茨海默病最近被证明与组蛋白乳酸化有关。Pan等 ADDIN EN.CITE ADDIN EN.CITE.DATA [12]首次在阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠和阿尔茨海默病患者脑组织样本中检测到高水平的组蛋白乳酸化,并确定组蛋白H4赖氨酸12乳酸化(H4K12la)水平的升高主要发生在β淀粉样蛋白斑块附近的小胶质细胞中。研究发现,H4K12la富集在小胶质细胞中糖酵解基因(如丙酮酸激酶PKM2)的启动子附近,激活其转录,从而增加糖酵解活性和乳酸生成,加重阿尔茨海默病小胶质细胞功能障碍,最终形成“糖酵解/H4K12la/PKM2”的正反馈调节回路。这种正反馈循环加剧了小胶质细胞稳态失衡和神经炎症的发生,从而促进了阿尔茨海默病的发展。紫草素等小分子靶向抑制PKM2可明显阻断正反馈调节回路,有效减少阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠淀粉样蛋白β斑块数量,提高小鼠的学习和认知能力,这一结果也提示抑制这种恶性循环可能是治疗阿尔茨海默病的有效策略。Hagihara等 ADDIN EN.CITE ADDIN EN.CITE.DATA [13]发现乳酸化程度与乳酸水平相关,神经元兴奋和社会失败应激可上调脑细胞的乳酸水平和乳酸化水平,证实了大脑中存在蛋白质乳酸化,可能在乳酸调节神经元活动方面发挥重要作用。单羧酸转运蛋白1是促进缺血后组织再生的关键转录调节因子,有助于新生小鼠脑缺氧缺血后的脑功能的恢复 ADDIN EN.CITE ADDIN EN.CITE.DATA [14],缺血期间内源性乳酸的产生改善了神经系统疾病的预后。此外,在进行性多发性硬化 ADDIN EN.CITE ADDIN EN.CITE.DATA [15]、癫痫、脑卒中 ADDIN EN.CITE ADDIN EN.CITE.DATA [5, 16]及胶质母细胞瘤 ADDIN EN.CITE ADDIN EN.CITE.DATA [17]中均发现,乳酸诱导的组蛋白乳酸化与神经退行性疾病及肿瘤中存在密切联系(表1),进一步研究乳酸-组蛋白乳酸化与这些神经退行性疾病之间的关系,可能会产生有趣的发现。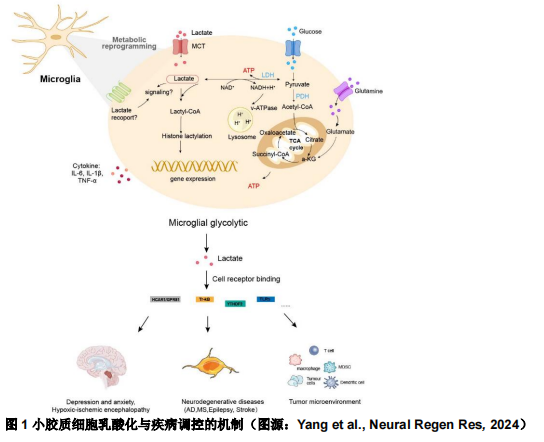
糖酵解和乳酸积累增加是各种类型癌症的共同特征。随着对乳酸生成和免疫调节在肿瘤中的作用的进一步认识,研究者发现许多靶向治疗方法。通过调节乳酸来调节肿瘤代谢的目前有两种策略。一种是通过抑制乳酸脱氢酶,非甾体抗炎药双氯芬酸已被证明可以独立于环氧化酶抑制调节糖酵解,并可用于改善抗程序性死亡受体1免疫治疗。第二种是通过靶向其出口来减少肿瘤微环境中的乳酸,乳酸主要是通过单羧酸转运蛋白运输的,值得庆幸的是,靶向单羧酸转运蛋白1和单羧酸转运蛋白4的药物目前处于临床前研究。例如阿斯利康的单羧酸转运蛋白1抑制剂AZD3956(NCT01791595)。临床前研究表明,AZD3965通过阻断单羧酸转运蛋白4以减少乳酸分泌到肿瘤微环境,增加肿瘤免疫细胞浸润;非甾体抗炎药双氯芬酸作为单羧酸转运蛋白4抑制剂,通过阻断单羧酸转运蛋白4来减少乳酸分泌 ADDIN EN.CITE ADDIN EN.CITE.DATA [22, 23]。
免疫调节药物(IMiDs),如沙利度胺及其衍生物来那度胺和泊马度胺,以其严重致畸性而受到人们的关注。事实上,IMiDs还具有多种抗肿瘤作用(包括抗血管生成和抗侵袭)。CD147(一种跨膜糖蛋白)与单羧酸转运蛋白1形成CD147-单羧酸转运蛋白1复合物,参与细胞代谢,尤其是糖酵解的调节。研究表明,IMiDs可以与CD147和单羧酸转运蛋白1竞争CRBN(IMiDs介导的抗癌和致畸的主要靶点)的结合,影响CD147-单羧酸转运蛋白1复合物的稳定性,从而发挥抗肿瘤作用。微环境缺氧是髓系恶性肿瘤的主要特征,髓系恶性肿瘤需要厌氧糖酵解来产生能量,因此乳酸输出至关重要,IMiDs诱导的CD147失稳和随后的T细胞负调控抑制可能有助于免疫细胞激活 ADDIN EN.CITE ADDIN EN.CITE.DATA [24]。
此外,高度糖酵解肿瘤代谢与治疗耐药有关,如多发性骨髓瘤和非小细胞肺癌。一方面,酸性环境中的肿瘤会形成保护屏障,阻止药物通过细胞膜。另一方面,在缺氧或酸中毒时,p-糖蛋白升高,将化疗药物泵出细胞。p-糖蛋白是一种活性药物转运蛋白,防止毒素或有害物质进入大脑,在许多肿瘤中的过度表达导致多种耐药表型。研究表明,p-糖蛋白通过调节小胶质细胞激活和介导免疫细胞迁移参与中枢神经系统疾病的免疫炎症反应。在缺氧和酸中毒的情况下,p-糖蛋白的活性增加,p-糖蛋白介导的细胞毒性药物如阿霉素和紫杉醇的外排明显增加,将药物泵出细胞,这很好地解释了化疗药物在缺氧/酸性肿瘤中的细胞毒性降低 ADDIN EN.CITE ADDIN EN.CITE.DATA [25]。由此发现,抗糖酵解同时抑制乳酸化可能会提高治疗效果,这种方法目前正在临床试验中进行测试(NCT01748500,
NCT01069081, NCT01163903)。靶向乳酸代谢可能是一种有用且有前途的治疗策略,研究有望开发出更有针对性且毒性更小的药物。
综述也存在一定性局限性。首先,由于目前小胶质细胞乳酸化在中枢神经系统疾病中的研究较少,机制还需要进一步的研究,通过更多的实验进行探索和验证。同时,外周神经系统的及肿瘤疾病中也可能受到小胶质细胞乳酸化的调节。其次,尽管已有研究表明,乳酸化作用在许多疾病、胚胎发育和神经调节中发挥作用,但对蛋白质的乳酸化作用的研究仍处于初级阶段,许多关键问题尚未解决。蛋白质的乳酸化是高乳酸积累的必然结果还是受时间和空间控制的精细调节?是否存在特定的乳酸化“Writer”或“Eraser”?目前仅确定赖氨酸残基为乳酸化的唯一位点,乳酸化是否发生在赖氨酸以外的其他氨基酸残基上?此外,在同一位点不同的酰化之间竞争、串扰和功能相互作用又是如何?仍是一些待解决的问题。尽管目前还有一些分歧,但蛋白质乳酸化的发现让人们重新认识到乳酸不单单是代谢的副产物,它的积累会影响机体的表观遗传修饰,同时也让乳酸化这一新型表观修饰进入了大众的视野,将细胞代谢与表观遗传调控联系起来。总之,这篇综述总结了小胶质细胞乳酸化机制及在中枢神经系统疾病中的研究,为更全面研究乳酸化机制提供思路。靶向乳酸代谢和乳酸化正在成为一种前景广阔的治疗策略。乳酸化的发现给乳酸的作用带来了新的生物学和功能方面的考虑。因此,未来仍需要进一步研究乳酸化的综合机制,揭示代谢与表观修饰之间的联系,以确定更多有利于药物研发的靶点。
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-23-00805
参考文献
[1] Salter MW, Stevens B. Microglia emerge as central players in brain disease. Nat Med. 2017;23(9):1018-1027.
[2] Kabba JA, Xu Y, Christian H, et al. Microglia: housekeeper of the central nervous system. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2018;38(1):53-71.
[3] Schurr A. Lactate: the ultimate cerebral oxidative energy substrate? J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2006;26(1):142-152.
[4] Schurr A. Lactate: a major and crucial player in normal function of both muscle and brain. J Physiol. 2008;586(11):2665-2666.
[5] Li R, Yang Y, Wang H, et al. Lactate and lactylation in the brain: current progress and perspectives. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023;43(6):2541-2555.
[6] Magistretti PJ, Allaman I. Lactate in the brain: from metabolic end-product to signalling molecule. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2018;19(4):235-249.
[7] Fischer K, Hoffmann P, Voelkl S, et al. Inhibitory effect of tumor cell-derived lactic acid on human T cells. Blood. 2007;109(9):3812-3819.
[8] Gottfried E, Kunz-Schughart LA, Ebner S, et al. Tumor-derived lactic acid modulates dendritic cell activation and antigen expression. Blood. 2006;107(5):2013-2021.
[9] Brand A, Singer K, Koehl GE, et al. LDHA-associated lactic acid production blunts tumor immunosurveillance by T and NK cells. Cell Metab. 2016;24(5):657-671.
[10] Cluntun AA, Huang H, Dai L, et al. The rate of glycolysis quantitatively mediates specific histone acetylation sites. Cancer Metab. 2015;3:10.
[11] Li X, Yang Y, Zhang B, et al. Lactate metabolism in human health and disease. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):305.
[12] Pan RY, He L, Zhang J, et al. Positive feedback regulation of microglial glucose metabolism by histone H4 lysine 12 lactylation in Alzheimer's disease. Cell Metab. 2022;34(4):634-648.e636.
[13] Hagihara H, Shoji H, Otabi H, et al. Protein lactylation induced by neural excitation. Cell Rep. 2021;37(2):109820.
[14] Kennedy L, Glesaaen ER, Palibrk V, et al. Lactate receptor HCAR1 regulates neurogenesis and microglia activation after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Elife. 2022;11.
[15] Wang X, Chang L, Wan X, et al. (R)-ketamine ameliorates demyelination and facilitates remyelination in cuprizone-treated mice: A role of gut-microbiota-brain axis. Neurobiol Dis. 2022;165:105635.
[16] Dong F, Liu Y, Yan W, et al. Netrin-4: focus on its role in axon guidance, tissue stability, angiogenesis and tumors. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023;43(5):1663-1683.
[17] Longhitano L, Vicario N, Forte S, et al. Lactate modulates microglia polarization via IGFBP6 expression and remodels tumor microenvironment in glioblastoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2023;72(1):1-20.#br#
[18] Pan RY, Ma J, Kong XX, et al. Sodium rutin ameliorates Alzheimer's disease-like pathology by enhancing microglial amyloid-β clearance. Sci Adv. 2019;5(2):eaau6328.
[19] Pan RY, He L, Zhang J, et al. Positive feedback regulation of microglial glucose metabolism by histone H4 lysine 12 lactylation in Alzheimer's disease. Cell Metab. 2022;34:634-648.e6(4).
[20] Wentling M, Lopez-Gomez C, Park HJ, et al. A metabolic perspective on CSF-mediated neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis. Brain. 2019;142(9):2756-2774.
[21] Kennedy L, Glesaaen ER, Palibrk V, et al. Lactate receptor HCAR1 regulates neurogenesis and microglia activation after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Elife. 2022;11:e76451.
[22] Marchiq I, Le Floch R, Roux D, et al. Genetic disruption of lactate/H+ symporters (MCTs) and their subunit CD147/BASIGIN sensitizes glycolytic tumor cells to phenformin. Cancer Res. 2015;75(1):171-180.
[23] Payen VL, Mina E, Van Hée VF, et al. Monocarboxylate transporters in cancer. Mol Metab. 2020;33:48-66.
[24] Eichner R, Heider M, Fernández-Sáiz V, et al. Immunomodulatory drugs disrupt the cereblon-CD147-MCT1 axis to exert antitumor activity and teratogenicity. Nat Med. 2016;22(7):735-743.
[25] Huang L, Li B, Li X, et al. Significance and mechanisms of P-glycoprotein in central nervous system diseases. Curr Drug Targets. 2019;20(11):1141-1155.

