NRR:山东第一医科大学宁文婧及徐玉振团队报道小胶质细胞在蛛网膜下出血中的作用
撰文:宁文婧
蛛网膜下腔出血是一种由颅内血管破裂和血液直接流入蛛网膜下腔引起的临床疾病,病死率很高,是一种毁灭性疾病,发病机制是十分复杂且多因素的[1, 2]。这一病症不仅在神经系统中引起生理和结构上的变化,同时也对患者的生命质量和预后产生深远的影响[3]。
小胶质细胞代表脑实质的常驻免疫细胞,是脑和脊髓中的实质巨噬细胞,与血管周围巨噬细胞一样,属于先天免疫系统,占神经胶质细胞总数的10%-15%。小胶质细胞是对各种急性脑损伤做出反应的关键免疫细胞,与中枢神经系统中的神经元、星形胶质细胞和少突胶质细胞等多种细胞相互作用[4]。
越来越多的研究表明,小胶质细胞具有多种功能,如维持神经环境平衡、支持神经元、介导细胞凋亡、参与免疫调节以及神经保护作用[5-7]。小胶质细胞在蛛网膜下腔出血的发病机制中发挥着关键作用,可影响着蛛网膜下腔出血的损伤及预后,且在蛛网膜下腔出血恢复期也发挥着一定的的神经保护作用[8]。一些旨在调节小胶质细胞功能的方法有望减轻蛛网膜下腔出血损伤,这为蛛网膜下腔出血的治疗提供新的靶点和思路。然而,对于小胶质细胞在蛛网膜下腔出血后作用仍缺乏深入而全面的总结。
中国山东第一医科大学第二附属医院徐玉振团队在《中国神经再生研究(英文)》(Neural Regeneration Research)上发表了题为“The pivotal role of microglia in injury and the prognosis of subarachnoid hemorrhage”的综述,总结了蛛网膜下腔出血后小胶质细胞的激活以及在血管痉挛、神经炎症、神经元凋亡、血脑屏障破坏、脑水肿和脑白质病变等病理过程中的作用,还讨论了小胶质细胞在蛛网膜下腔出血恢复阶段的神经保护作用以及针对调节蛛网膜下腔出血后小胶质细胞功能的治疗进展。这可能为蛛网膜下腔出血未来的转化治疗提供一些新的治疗线索和思路,以减轻蛛网膜下腔出血后的损害。
蛛网膜下腔出血是世界范围内发病率和死亡率较高的一种重要的公共卫生问题。蛛网膜下腔出血致残率高、病死率高,约30%-50%的蛛网膜下腔出血幸存者出现迟发性神经功能障碍[9],导致患者生活质量严重下降和社会经济负担增加。
小胶质细胞代表脑实质的常驻免疫细胞,是脑和脊髓中的实质巨噬细胞,与血管周围巨噬细胞一样,属于先天免疫系统,占神经胶质细胞总数的10%-15%。小胶质细胞是对各种急性脑损伤做出反应的关键免疫细胞,可与中枢神经系统中的许多其他细胞相互作用,对于维持中枢神经系统环境的稳态、支持神经元功能和参与免疫调节等方面发挥着至关重要的作用[4]。
正常情况下,小胶质细胞呈高度分枝状,具有三级和四级分枝结构,且细胞间的分枝很少发生重叠,这种分枝状的小胶质细胞通常被称为“静息型”小胶质细胞[10]。当脑内发生炎症、感染、创伤或其他神经系统疾病时,小胶质细胞迅速被激活呈活化形式并获得吞噬功能。激活的小胶质细胞胞体增大、突起变短、细胞形态呈圆形或杆状。进一步激活和调整的小胶质细胞,其突起消失、细胞形态呈阿米巴状,并具有较强的吞噬功能[11]。
小胶质细胞活化形式包括M1型(经典激活型)和M2型(选择激活型)2种亚型,而M2型进一步分为M2a型(再生修复型)、M2b型(免疫调节型)和M2c型(获得钝化型)[12];M1型和M2型对于神经细胞分别具有细胞毒性和细胞保护的作用,形成了一个复杂的激活机制[13]。
小胶质细胞还能够感知外部环境的变化,并随后调整其在内部微环境中的角色,其缺点是促炎性小胶质细胞对原发性神经元或轴突变性以及与全身炎症相关的其他过程的过度激活可能引发或维持慢性炎症,导致长期的神经功能损伤[13, 14](图1)。
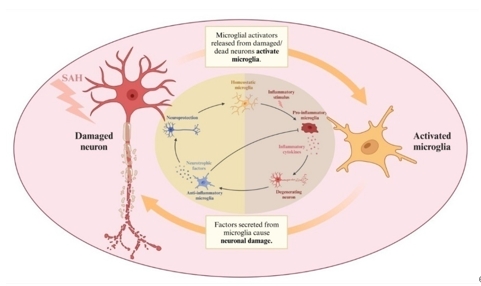
图1小胶质细胞和神经元损伤(图源:Ning et al., Neural Regen Res, 2025)
在蛛网膜下腔出血后24h内,小胶质细胞显示出激活的形态学迹象[12]。M1型小胶质细胞相关标记物白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α显著增加[12]。有研究表明,在蛛网膜下腔出血后24h内皮质中就存在活化的小胶质细胞,而72h后才逐渐出现单核细胞的浸润,至少在蛛网膜下腔出血后的前48h,早期神经炎症反应主要由驻留的小胶质细胞启动和加强[15]。在这个急性期间,小胶质细胞的激活状态是M1型,被认为是促炎的,其促炎作用促进了细胞的死亡,包括神经元的坏死性凋亡[12]。神经元的坏死性凋亡和坏死导致了炎症分子(警报分子,如高迁移率族蛋白1)的进一步释放,这进一步激活了小胶质细胞的大量活化,小胶质细胞的活化导致血源性先天性炎症细胞的招募,血脑屏障的通透性增加和神经元损失的增加[16]。
在蛛网膜下腔出血后24-72h,活化的小胶质细胞急性表达p75神经营养因子受体,以帮助追踪小胶质细胞浸润的时间进程,研究显示小胶质细胞在此阶段的活化数量较前进一步增加[15]。
M1小胶质细胞的增加趋势的转折点是蛛网膜下腔出血后的第3天,而后M1小胶质细胞数量开始下降,而M2标记物也在蛛网膜下腔出血后的第3天开始增加[12, 17]。在这个时间段内,小胶质细胞的聚集和激活,对脑实质产生了促炎效应,诱导神经元凋亡,导致了长期的神经损伤[12]。
在蛛网膜下腔出血后第4-6天,小胶质细胞的激活程度低于24h,但高于基线,而后逐渐增加,在第14天左右达到第2次峰值,然后在第28天附近逐渐消退。小胶质细胞在初始激活(24h)、恢复到基线(3d)和再激活(14d)之间发生动态变化[12, 17]。在第14-28天,小胶质细胞中白细胞介素6、Toll样受体4和肿瘤坏死因子α表达增加[18]。在蛛网膜下腔出血晚期,全脑中M2相关基因白细胞介素4和转化生长因子β上调[19]。炎症细胞因子的表达谱与小细胞极化的动态变化相同。这些免疫调节剂已被证明小胶质细胞的激活可破坏血脑屏障,招募额外的外周免疫细胞,诱发神经炎症,继而造成神经损伤[18, 20](图2)。
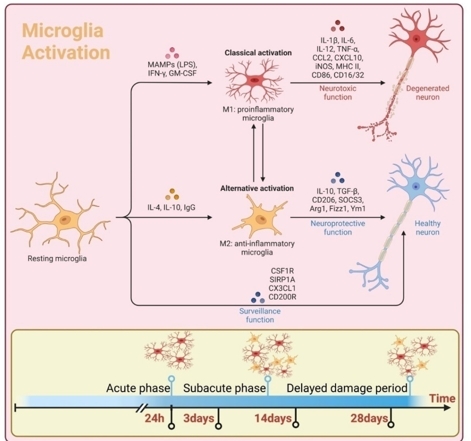
图2蛛网膜下腔出血后小胶质细胞的激活(图源:Ning et al., Neural Regen Res, 2025)
血管痉挛是蛛网膜下腔出血后的一种致命并发症。既往的研究已证明,小胶质细胞和Toll样受体4均参与蛛网膜下腔出血的早期和晚期阶段,可触发血管痉挛[21]。M1小胶质细胞在脑血管痉挛的发病机制中起关键作用,其释放的炎性产物还导致脑实质损伤,破坏血脑屏障,促进水肿,增加颅内压,降低脑灌注压,可能导致继发性缺血性损伤,以及导致大脑自我调节功能障碍,可能导致脑缺血或充血[22]。
小胶质细胞在蛛网膜下腔出血中诱导神经元凋亡,其表达的Toll样受体4被高迁移率族蛋白1、血红素和高铁血红蛋白等配体激活,进而通过接头蛋白介导一系列下游信号通路。这一途径产生致炎细胞因子和氧化代谢产物,导致神经元凋亡和组织损伤[21, 23]。小胶质细胞在蛛网膜下腔出血后神经细胞凋亡中发挥重要的调控作用,也是蛛网膜下腔出血治疗的关键分子靶点,但关于小胶质细胞与神经细胞凋亡更多具体的机制有待于进一步的研究。
中枢神经系统的炎症主要由小胶质细胞介导,这些细胞在遇到炎症刺激时会激活并触发炎症级联反应[24]。小胶质细胞可能表现出促炎或抗炎特性,被描述为M1和M2表型[13]。其中M1小胶质细胞是由干扰素γ、肿瘤坏死因子和病原体相关分子模式诱导的促炎细胞,而M2小胶质细胞通过调节抗炎反应来化解炎症,促进组织修复和重塑。蛛网膜下腔出血后,小胶质细胞数量增加,M1最初占主导地位,但随后逐渐转变为M2表型[10, 11]。
蛛网膜下腔出血引起的神经炎症可通过激活的小胶质细胞的侵袭从大脑的前部到后部扩散到大脑皮质的所有层,且神经元死亡与神经炎症相关。这种趋势随着疾病的严重程度而增加。大脑皮质负责长期记忆和运动,抑制大脑皮质的神经炎症可能会改善蛛网膜下腔出血预后[25]。
血脑屏障是人体的重要生理屏障。当其受损时,炎性物质和血浆成分更容易进入脑实质,加剧神经炎症和脑损伤,导致大脑功能障碍[26]。在蛛网膜下腔出血后,与Toll样受体4/MyD88信号通路相关的MAPK被激活,进一步增加细胞因子的释放,导致血脑屏障的破坏[27]。钙敏感受体激活可导致神经恶化、脑水肿和神经变性。抑制钙敏感受体激活和NLRP3炎症小体的产生,可改善蛛网膜下腔出血后的神经功能障碍、脑水肿和血脑屏障破坏。
当血管暴露于病理生理应激源时,血管激活、血脑屏障破坏和小胶质细胞向M1激活状态的转变之间似乎存在非常精确和紧密的时空相关性[19, 28]。目前的数据表明,M1促炎小胶质细胞参与血脑屏障功能障碍和血管“渗漏”,而M2抗炎小胶质细胞在血脑屏障中起保护作用[29]。持续的炎症触发激活的小胶质细胞诱导血脑屏障的损伤[30]。小胶质细胞也可直接与内皮细胞相互作用,影响血脑屏障的通透性[31]。
蛛网膜下腔出血患者和动物模型中的证据都表明,在蛛网膜下腔出血后的早期磁共振成像可见异常的白质信号[32],甚至在超急性期(4h内),表明了白质损伤的存在[33]。在脑损伤急性期,小胶质细胞快速响应并释放与损伤相关的模式分子诱导脑白质损伤,小胶质细胞在中枢神经系统髓鞘健康和再生的调节中也发挥着至关重要的作用[34]。白质损伤会导致蛛网膜下腔出血后严重的认知功能障碍、情绪障碍等。越来越多的研究描述了小胶质细胞与蛛网膜下腔出血后的白质损伤的密切关系。
小胶质细胞在中枢神经系统创伤后不仅可释放促炎因子和细胞毒性物质,造成神经元损伤和凋亡,而且可通过吞噬作用清除细胞碎片,并释放神经生长及抗炎因子从而减轻神经损伤,促进组织修复,发挥神经保护作用[35-37]。
M2型小胶质细胞在过敏反应、寄生虫清除、抑制炎症、组织重塑和免疫调节中起作用。在蛛网膜下腔出血中,M2小胶质细胞的功能主要是通过抑制炎症来促进损伤的修复,M2小胶质细胞主要出现在早期脑损伤的伤害晚期[12, 15]。在早期脑损伤期间,小胶质细胞的激活促进了一系列神经保护蛋白的形成,如神经珠蛋白和血红素氧合酶1。神经保护蛋白可通过减少氧化应激来保护神经元[38](图3)。
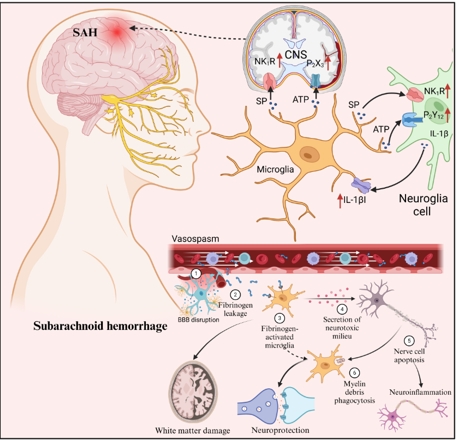
图3小胶质细胞在蛛网膜下腔出血中的功能(图源:Ning et al., Neural Regen Res, 2025)
虽然蛛网膜下腔出血后激活的小胶质细胞炎症通路很复杂,但大量的研究已进行,因而对小胶质细胞作用具体的机制尚无定论,但其中已涉及一些已知的传统细胞信号级联反应和一些通过部分验证的药物发挥作用,最终改善蛛网膜下腔出血的症状及预后。
蛛网膜下腔出血的发病机制复杂,临床症状严重,预后差。小胶质细胞是中枢神经系统的重要组成部分,在蛛网膜下腔出血的发病机制和预后中起着重要作用。小胶质细胞作用机制复杂,涉及分子及通路众多,徐玉振等总结了小胶质细胞如何在蛛网膜下腔出血期间被激活并参与血管痉挛、神经炎症、神经细胞凋亡、血脑屏障破坏和脑水肿以及脑白质损伤等病理过程,以及小胶质细胞在蛛网膜下腔出血恢复期发挥的神经保护作用。尽管经过几十年的探索,蛛网膜下腔出血的预后仍远不能令人满意,给患者和社会带来了沉重的负担,关于蛛网膜下腔出血治疗的研究从未中止,文章也对近年蛛网膜下腔出血针对小胶质细胞的治疗方法进行了全面的分类总结,以期为蛛网膜下腔出血的治疗带来一定的帮助。文章描述的大部分方法尚停留在实验室阶段,更多蛛网膜下腔出血的临床研究和数据仍需要被收集,为将来蛛网膜下腔出血治疗的临床转化奠定基础。
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-00241
参考文献:
[1] Muehlschlegel S. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Continuum (Minneap Minn). 2018;24(6):1623-1657.
[2] Ziu E, Khan Suheb MZ, Mesfin FB. Subarachnoid hemorrhage. In: StatPearls. 2024. StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island (FL).
[3] Macdonald RL, Schweizer TA. Spontaneous subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet. 2017;389(10069):655-666.
[4] Prinz M, Jung S, Priller J. Microglia biology: one century of evolving concepts. Cell. 2019;179(2):292-311.
[5] Jia X, Gao Z, Hu H. Microglia in depression: current perspectives. Sci China Life Sci. 2021;64(6):911-925.
[6] Wang XY, Wu F, Zhan RY, et al. Inflammatory role of microglia in brain injury caused by subarachnoid hemorrhage. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022;16:956185.
[7] Subhramanyam CS, Wang C, Hu Q, et al. Microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019;94:112-120.
[8] Xia DY, Yuan JL, Jiang XC, et al. SIRT1 promotes M2 microglia polarization via reducing ROS-mediated nlrp3 inflammasome signaling after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Front Immunol. 2021;12:770744.
[9] Chou SH. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Continuum (Minneap Minn). 2021;27(5):1201-1245.
[10] Rodríguez-Gómez JA, Kavanagh E, Engskog-Vlachos P, et al. Microglia: agents of the CNS Pro-Inflammatory Response. Cells. 2020;9(7):1717.
[11] Colonna M, Butovsky O. Microglia function in the central nervous system during health and neurodegeneration. Annu Rev Immunol. 2017;35:441-468.
[12] Chen J, Wong GKC. Microglia accumulation and activation after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(8):1531-1532.
[13] Kwon HS, Koh SH. Neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative disorders: the roles of microglia and astrocytes. Transl Neurodegener. 2020;9(1):42.
[14] Hickman S, Izzy S, Sen P, et al. Microglia in neurodegeneration. Nat Neurosci. 2018;21(10):1359-1369.
[15] Xu Z, Shi WH, Xu LB, et al. Resident microglia activate before peripheral monocyte infiltration and p75NTR blockade reduces microglial activation and early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2019;10(1):412-423.
[16] Zeyu Z, Yuanjian F, Cameron L, et al. The role of immune inflammation in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Exp Neurol. 2021;336:113535.
[17] Chen J, Zheng ZV, Lu G, et al. Microglia activation, classification and microglia-mediated neuroinflammatory modulators in subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(7):1404-1411.
[18] Timis TL, Florian IA, Susman S, et al. Involvement of microglia in the pathophysiology of intracranial aneurysms and vascular malformations-a short overview. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(11):6141.
[19] Wang C, Jia Q, Sun C, et al. Calcium sensing receptor contribute to early brain injury through the CaMKII/NLRP3 pathway after subarachnoid hemorrhage in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;530(4):651-657.
[20] Schneider UC, Xu R, Vajkoczy P. Inflammatory events following subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018;16(9):1385-1395.
[21] Wang L, Geng G, Zhu T, et al. Progress in research on TLR4-mediated inflammatory response mechanisms in brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Cells. 2022;11(23):3781.
[22] Wu CH, Tsai HP, Su YF, et al. 2-PMAP ameliorates cerebral vasospasm and brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage by regulating neuro-inflammation in rats. Cells. 2022;11(2):242.
[23] Mathy NW, Burleigh O, Kochvar A, et al. A novel long intergenic non-coding RNA, Nostrill, regulates iNOS gene transcription and neurotoxicity in microglia. J Neuroinflammation. 2021;18(1):16.
[24] Jin J, Duan J, Du L, et al. Inflammation and immune cell abnormalities in intracranial aneurysm subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH): Relevant signaling pathways and therapeutic strategies. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1027756.
[25] Yamada H, Kase Y, Okano Y, et al. Subarachnoid hemorrhage triggers neuroinflammation of the entire cerebral cortex, leading to neuronal cell death. Inflamm Regen. 2022;42(1):61.
[26] Alahmari A. Blood-brain barrier overview: structural and functional correlation. Neural Plast. 2021;2021:6564585.
[27] Liu FY, Cai J, Wang C, et al. Fluoxetine attenuates neuroinflammation in early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage: a possible role for the regulation of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. J Neuroinflammation. 2018;15(1):347.
[28] Bowyer JF, Sarkar S, Tranter KM, et al. Vascular-directed responses of microglia produced by methamphetamine exposure: indirect evidence that microglia are involved in vascular repair? J Neuroinflammation. 2016;13(1):64.
[29] Haruwaka K, Ikegami A, Tachibana Y, et al. Dual microglia effects on blood brain barrier permeability induced by systemic inflammation. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):5816.
[30] Kang R, Gamdzyk M, Lenahan C, et al. The dual role of microglia in blood-brain barrier dysfunction after stroke. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2020;18(12):1237-1249.
[31] Ronaldson PT, Davis TP. Regulation of blood-brain barrier integrity by microglia in health and disease: A therapeutic opportunity. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2020;40(1_suppl):S6-S24.
[32] Luo K, Yang L, Liu Y, et al. HDAC inhibitor SAHA alleviates pyroptosis by up-regulating miR-340 to inhibit NEK7 signaling in subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurochem Res. 2023;48(2):458-470.
[33] Reijmer YD, Van Den Heerik MS, Heinen R, et al. Microstructural white matter abnormalities and cognitive impairment after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 2018;49(9):2040-2045.
[34] Toyota Y, Wei J, Xi G, et al. White matter T2 hyperintensities and blood-brain barrier disruption in the hyperacute stage of subarachnoid hemorrhage in male mice: the role of lipocalin-2. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019;25(10):1207-1214.
[35] Nakajima K, Kohsaka S. Microglia: neuroprotective and neurotrophic cells in the central nervous system. Curr Drug Targets Cardiovasc Haematol Disord. 2004;4(1):65-84.
[36] Chen Z, Trapp BD. Microglia and neuroprotection. J Neurochem. 2016;136 Suppl 1:10-17.
[37] Gupta DP, Park SH, Lee YS, et al. Daphne genkwa flower extract promotes the neuroprotective effects of microglia. Phytomedicine. 2023;108:154486.
[38] Sozen T, Tsuchiyama R, Hasegawa Y, et al. Immunological response in early brain injury after SAH. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2011;110(Pt 1):57-61.


