NRR:空军军医大学西京医院王化宁和才延辉团队阐述脑乳酸作为精神疾病治疗靶点的可能
长期以来的观点是乳酸只是缺氧条件下的一种代谢废物,而近年来研究发现,乳酸还具有多种生理功能,同时也是一种重要的胶质-神经元递质,可在多种精神疾病中发生显著的变化。
最近,来自中国空军军医大学西京医院心身科王化宁教授和才延辉教授团队在《中国神经再生研究(英文版)》(Neural Regeneration Research)上发表了题为“Lactate: a prospective target for therapeutic intervention in psychiatric disease”的综述。该文章从神经递质在精神药物中的作用出发,指出靶向新型神经递质的药物是治疗精神疾病的一个很有前途的策略,基于此探讨了乳酸作为信号分子及其相关信号通路的研究进展,描述了抑郁、焦虑、双相情感障碍和精神分裂中脑乳酸水平的变化,并指出脑乳酸做为精神药理学治疗目标的潜力和面临的挑战。这一综述全面总结了乳酸在精神疾病中的研究进展,展望了乳酸在精神药理学治疗中的潜在价值。
精神药物是治疗精神疾病的最基本疗法,且大多数精神药物都是以调节少数重要脑神经递质为目标,如血清素、多巴胺和去甲肾上腺素[1]。最近的证据表明,精神疾病涉及多个神经递质功能障碍[2]。基于此,目前部分患者的精神药物疗效不佳,可能与精神药物调节神经递质的范围有限相关。而针对被忽视的神经递质的新型精神药物可能对精神药物耐药性带来意想不到的影响,氯胺酮就是一个典型的例子。以前的抗抑郁药大多集中在单胺能系统,氯胺酮作为谷氨酸受体的非竞争性拮抗剂,能发挥快速抗抑郁作用[3]。这提示应该将精神药物治疗的目标转移到一个更全面的模式,尝试更多的可能性,以解决目前精神药理学的不足。
星形胶质细胞-神经元乳酸穿梭假说使人认识到,乳酸除了作为代谢物(图1)外还有其他作用。星形胶质细胞和少突胶质细胞可以通过单羧酸转运蛋白(MCT1/4)将乳酸转运到细胞外[4],细胞外乳酸既可以通过MCT2进入神经元[4],也可以直接与乳酸受体(羟基羧酸受体1,HCAR1))结合[5](图2)。星形胶质细胞来源的乳酸通过MCT受体和HCAR1在调节认知功能中发挥重要作用,包括突触传递、记忆形成和药物成瘾[6, 7]。另外值得注意的是,脑乳酸代谢不是一个自我循环系统,其他器官也可通过血液循环影响脑乳酸水平。研究发现,运动过程中肌肉细胞释放的乳酸可以进入血脑屏障,加速海马脑源性神经营养因子的表达,从而增强空间学习记忆的保持[8]。此外,运动诱导的乳酸上调通过HCAR1促进脑血管生成,延缓神经退行性变[9]。另有研究报道外周注射乳酸可通过单磷酸腺苷活化蛋白激酶/丙二酰辅酶A(AMPK/malonyl-CoA)途径抑制下丘脑食物摄取[10]。总的来说,胶质乳酸和外周乳酸诱导的脑功能变化进一步证实了乳酸的多重特性,尤其是作为信号分子的特性。 同时,乳酸衍生的“乳酸化” 做为表观遗传调节因子能调节基因转录[11]。
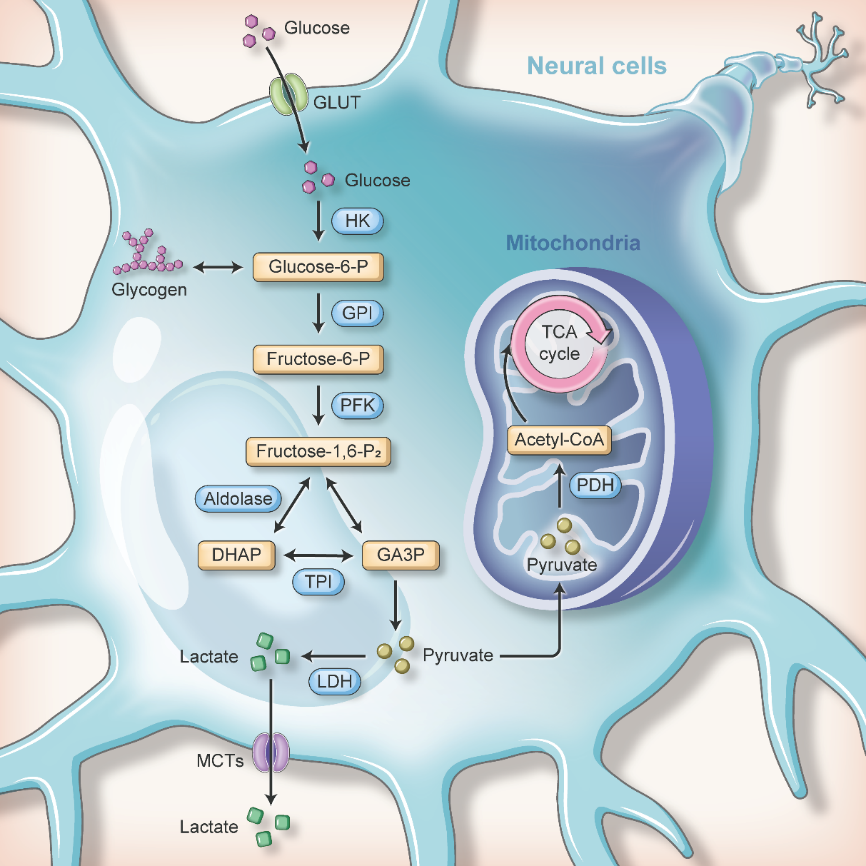
图1神经细胞乳酸代谢示意图(图源:Cai et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
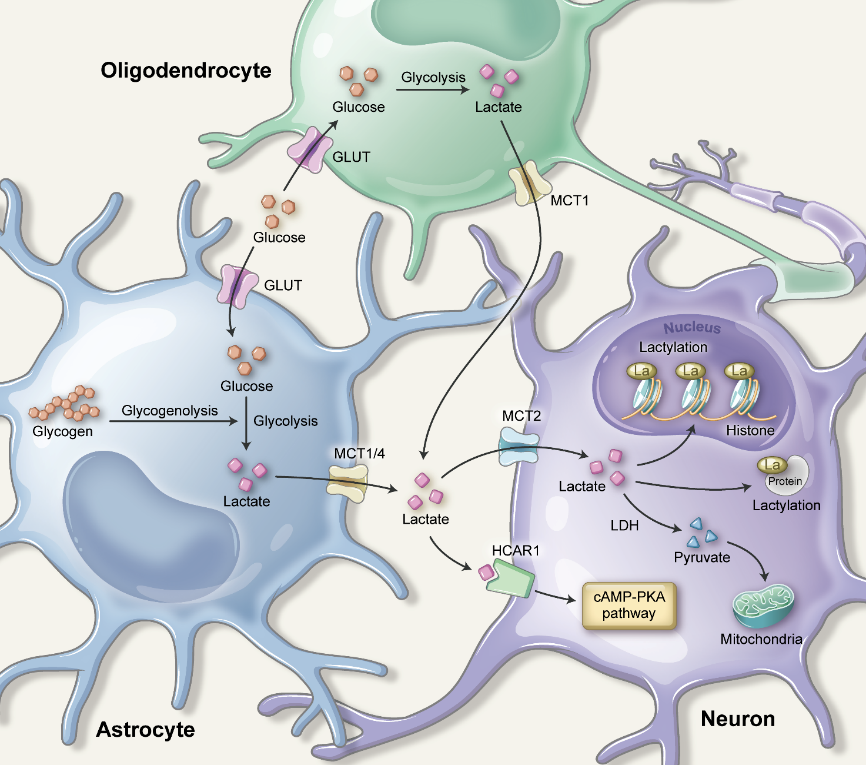
图2:脑乳酸作为一种新型神经胶质细胞神经递质示意图(图源:Cai et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
另外,脑乳酸水平在抑郁障碍、焦虑障碍、精神分裂症、双向情感障碍等精神疾病中发生显著改变,在动物抑郁模型和抑郁患者临床研究中分别发现,某些脑区乳酸水平显著增加,但外源性乳酸也有抗抑郁作用[12]。同时令人意外的是,多项研究表明外源性乳酸也具有致焦虑作用[13],其中的机制需要进一步探索。
许多研究发现脑乳酸不仅是一种代谢产物,而且可以通过调节神经元电活动来调节大脑功能,类似于“神经递质”。此外,许多精神疾病都有乳酸变化,外源性乳酸注射影响某些精神障碍如抑郁症的结局。基于这2个方面,王化宁和才延辉等得出脑乳酸是治疗精神疾病的潜在靶点之一。但是,需要特别注意,进一步阐明乳酸在精神疾病中变化的机制是乳酸作为精神药理学治疗靶点的基础。
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.387969
参考文献:#br#
[1] Siafis S, Tzachanis D, Samara M, et al. Antipsychotic drugs: from receptor-binding profiles to metabolic side effects. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018;16(8):1210-1223.
[2] Forray C, Buller R. Challenges and opportunities for the development of new antipsychotic drugs. Biochem Pharmacol. 2017;143:10-24.
[3] Zanos P, Gould TD. Mechanisms of ketamine action as an antidepressant. Mol Psychiatry. 2018;23(4):801-811.
[4] Bélanger M, Allaman I, Magistretti PJ. Brain energy metabolism: focus on astrocyte-neuron metabolic cooperation. Cell Metab. 2011;14(6):724-738.
[5] Liu C, Wu J, Zhu J, et al. Lactate inhibits lipolysis in fat cells through activation of an orphan G-protein-coupled receptor, GPR81. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(5):2811-2822.
[6] Briquet M, Rocher AB, Alessandri M, et al. Activation of lactate receptor HCAR1 down-modulates neuronal activity in rodent and human brain tissue. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2022;42(9):1650-1665.
[7] Wang Q, Hu Y, Wan J, et al. Lactate: A novel signaling molecule in synaptic plasticity and drug addiction. Bioessays. 2019;41(8):e1900008.
[8] El Hayek L, Khalifeh M, Zibara V, et al. Lactate mediates the effects of exercise on learning and memory through SIRT1-dependent activation of hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). J Neurosci. 2019;39(13):2369-2382.
[9] Morland C, Andersson KA, Haugen Ø P, et al. Exercise induces cerebral VEGF and angiogenesis via the lactate receptor HCAR1. Nat Commun. 2017;8:15557.
[10] Cha SH, Lane MD. Central lactate metabolism suppresses food intake via the hypothalamic AMP kinase/malonyl-CoA signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;386(1):212-216.
[11] Zhang D, Tang Z, Huang H, et al. Metabolic regulation of gene expression by histone lactylation. Nature. 2019;574(7779):575-580.
[12] Carrard A, Elsayed M, Margineanu M, et al. Peripheral administration of lactate produces antidepressant-like effects. Mol Psychiatry. 2018;23(2):392-399.
[13] Johnson PL, Fitz SD, Engleman EA, et al. Group II metabotropic glutamate receptor type 2 allosteric potentiators prevent sodium lactate-induced panic-like response in panic-vulnerable rats. J Psychopharmacol. 2013;27(2):152-161.

第一作者:才延辉,男,项目组负责人,现为第四军医大学西京医院心身科副教授,副主任医师,硕士研究生导师。中华医学会心身医学分会青年委员,中国医师协会精神科医师分会委员,陕西省国际医学交流促进会精神心理卫生专业委员会副主任委员,中国医药教育协会心理精神健康教育委员会委员,陕西省医师协会精神心理科分会委员。研究方向为神经代谢,近3年来以星形胶质细胞糖原代谢为突破口共发表SCI论文13篇,其中以第一作者或通讯作者发表SCI论文共8篇,大于5分5篇,单篇最高影响因子9.587。主持国家自然科学基金2项,院级课题3项。获得国家实用新型专利2项,参编专著2部,担任Bioengineered和Neural Regeneration Research杂志审稿人,相关研究成果受邀参与国际会议发言3次,国内会议发言3次,获得优秀壁报奖2次,受到本领域同行的广泛关注和认可。
王化宁副教授、郭海云博士为通讯作者。
韩天乐助教为共同第一作者。


