中国神经再生研究(英文版) ›› 2024, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (6): 1212-1220.doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.385850
长链非编码RNA在神经退行性疾病中的重要作用
Long non-coding RNAs with essential roles in neurodegenerative disorders
Wandi Xiong1, *, Lin Lu2, 3, 4, 5, Jiali Li1, 3, 4, *
- 1Key Laboratory of Animal Models and Human Disease Mechanisms of Chinese Academy of Sciences & Yunnan Province, Kunming Institute of Zoology, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Kunming, Yunnan Province, China; 2Tsinghua-Peking Center for Life Sciences, Beijing, China; 3National Institute on Drug Dependence, Peking University, Beijing, China; 4PKU/McGovern Institute for Brain Research, Peking University, Beijing, China; 5Institute of Mental Health, National Clinical Research Center for Mental Disorders, Key Laboratory of Mental Health and Peking University Sixth Hospital, Peking University, Beijing, China
摘要:
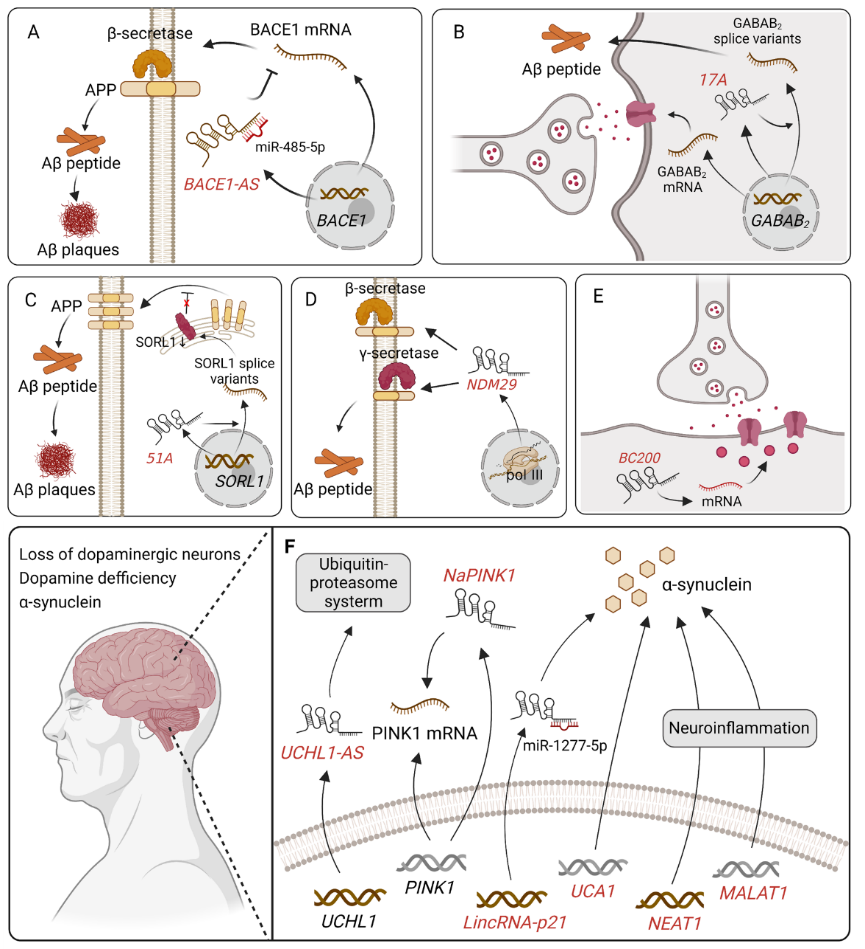
近年来,随着高分辨率和高通量测序技术的出现,越来越多的长链非编码RNA被发现以特定的时空模式参与中枢神经系统神经元功能的调节,甚至也参与不同神经退行性疾病。然而,长链非编码RNA在神经退行性变过程中的潜在机制仍然难以捉摸。因此,此次综述概述了长链非编码RNA生物学的研究进展,并重点介绍了长链非编码RNA阿尔茨海默病、帕金森病、亨廷顿病和肌萎缩侧索硬化中的最新作用、调控机制和研究现状。最后讨论了长链非编码RNA作为神经退行性疾病的诊断生物标志物和治疗靶点的潜在价值。希望为开发基于长链非编码RNA神经退行性疾病提供新的思路。
https://orcid.org/0009-0001-3229-4360 (Wandi Xiong); https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0039-3671 (Jiali Li)