NRR:嘉兴学院医学院贾金婧团队认为NLRP 3/1介导细胞焦亡可为阿尔茨海默病治疗提供线索
撰文:胡泊,张佳萍,黄杰,骆柏如,曾宪思,贾金婧
阿尔茨海默病是一种最常见的神经退行性疾病。阿尔茨海默病的临床特征是进行性认知能力下降、记忆力丧失和运动障碍,并伴有一系列精神症状[1]。有研究表明,氧化应激、内质网应激、线粒体功能障碍、基因突变、表观遗传学和神经炎症等与阿尔茨海默病的发病机制密切相关[2, 3]。神经炎症与脑神经元丢失的关系越来越引发人们的关注。含NLR家族Pyrin域蛋白3/1(NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3/1,NLRP3/NLRP1)炎症小体激活可导致神经炎症,分别引发小胶质细胞和神经元的焦亡。因此,NLRP3和NLRP1介导的细胞焦亡在阿尔茨海默病的发病过程中起着重要的作用。然而阿尔茨海默病中NLRP3和NLRP1介导的细胞焦亡仍缺乏深入而全面的总结。
最近来自中国嘉兴学院医学院贾金婧团队在《中国神经再生研究(英文版)》(Neural Regeneration Research)上发表了题为“NLRP3/1-mediated pyroptosis: beneficial clues for the development of novel therapies for Alzheimer’s disease”的综述。该文全面总结了阿尔茨海默病的潜在发病机制,并提出了神经炎症的重要性,进而综述了NLRP3和NLRP1的结构以及NLRP3与NLRP1激活在阿尔茨海默病中的作用。此外,文章还总结了小分子抑制剂、内源性抑制剂蛋白、微小RNA和天然活性成分通过抑制NLRP3或NLRP1对阿尔茨海默病发挥的神经保护作用。因此,抑制NLRP3和NLRP1炎症小体介导的细胞焦亡可能为建立阿尔茨海默病的新治疗策略提供有益的线索。
阿尔茨海默病中的神经炎症与炎症小体的激活密切相关。炎症小体通常包含传感器、适配器和半胱氨酸蛋白酶1前体[4]。各种炎症小体的核心结构由核苷酸结合结构域和富含亮氨酸重复序列(leucine-rich repeat,LRR)的受体(NLRs)、pyrin受体或黑色素瘤缺乏因子2受体组成。NLRP3和NLRP1炎症小体是中枢神经系统中重要且研究较为清楚的NLR炎症小体[4]。在过去的10年间,NLRP3和NLRP1炎症小体介导的神经退行性变已被证明可诱导细胞焦亡[5]。贾金婧等总结了NLRP3和NLRP1以及含有caspase-1激活和募集结构域(CARD)的凋亡相关斑点样蛋白(ASC)和caspase-1前体的结构 (图1)。人NLRP3和NLRP1均含有PYD、NACHT和LRR结构域,NLRP1还含有FIIND和CARD结构域。
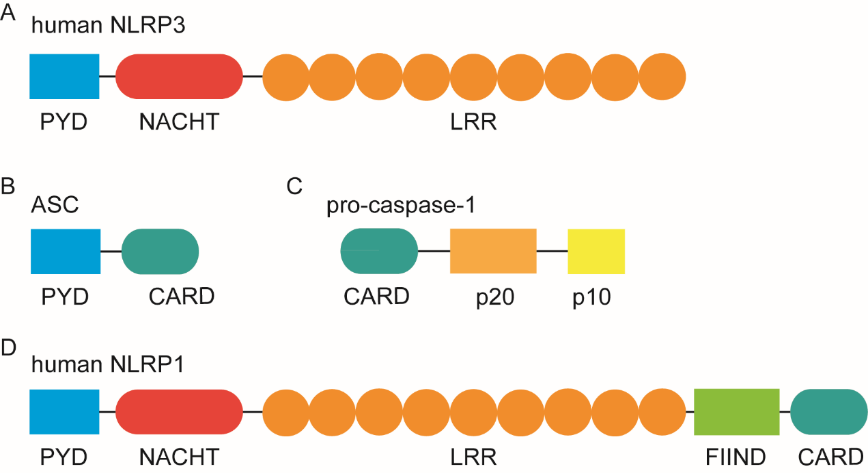
图1 NLRP3和NLRP1的结构(图源:Hu et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
NLRP3在中枢神经系统主要表达于小胶质细胞中,但其本底表达不足以激活NLRP3炎症小体。研究发现,NLRP3的激活需要两步过程,包括启动和激活阶段[6]。启动过程由Toll样受体或细胞因子受体(如白细胞介素1受体和肿瘤坏死因子受体)的激活诱导,随后与caspase-8和FAS相关死亡结构域蛋白(FAS-associated death domain protein,FADD)共同激活核因子kappa B(nuclear factor kappa-B,NF-κB)信号途径[7],并进一步导致NLRP3和白细胞介素1β前体的转录表达上调[8]。NLRP3的PYD结构域通过与ASC的PYD域的相互作用募集ASC。ASC的CARD结构域随后招募含有CARD结构域的caspase-1前体以形成复合体(NLRP3/ASC/caspase-1前体),即NLRP3炎症小体。NLRP3炎症小体组装和激活后,caspase-1前体自裂解为活性caspase-1,这进一步导致白细胞介素1β的成熟。此外,gasdermin D(GSDMD)也被caspase-1切割,GSDMD-N结构域形成跨膜孔,介导成熟白细胞介素1β的释放,并诱导一种炎症性细胞死亡,即细胞焦亡。NLRP3炎症小体激活的一般过程如图2所示。
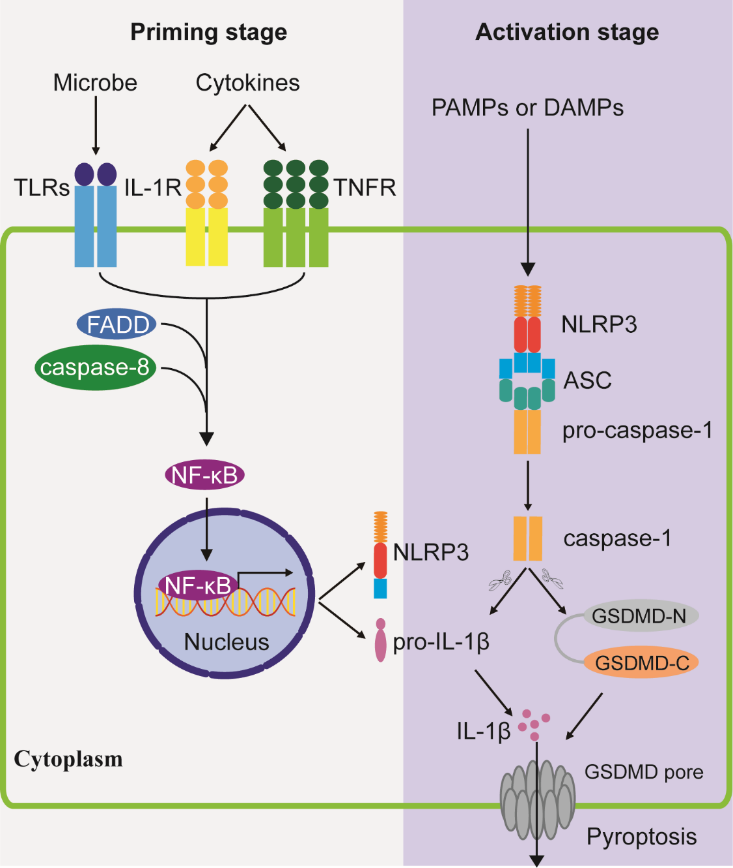
图2 NLRP3炎症小体活化及其介导的细胞焦亡(图源:Hu et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
NLRP1在中枢神经系统主要表达于神经细胞中。与NLRP3类似,NF-κB信号通路的激活也增加NLRP1转录表达。FIIND基序的翻译后自切割成两个断开的结构域(ZU5和UPA,通过非共价键连接)对于NLRP1的激活是必需的[9]。蛋白水解酶在PYD和NACHT结构域之间切割NLRP1的N末端是NLRP1激活的前提,表明NLRP1 N末端区域发挥自我抑制作用。位于NLRP1的NACHT结构域中的2个ATP结合基序是该炎症小体的自体寡聚和随后的组装所必需的。NLRP1炎症小体由NLRP1、ASC和caspase-1前体组成。NLRP1可以直接募集依赖于其C末端CARD结构域的caspase-1前体,以与caspase-1前体的CARD相互作用(图3)。有趣的是,ASC斑点形成可极大地增强人类NLRP1炎症小体的活性。
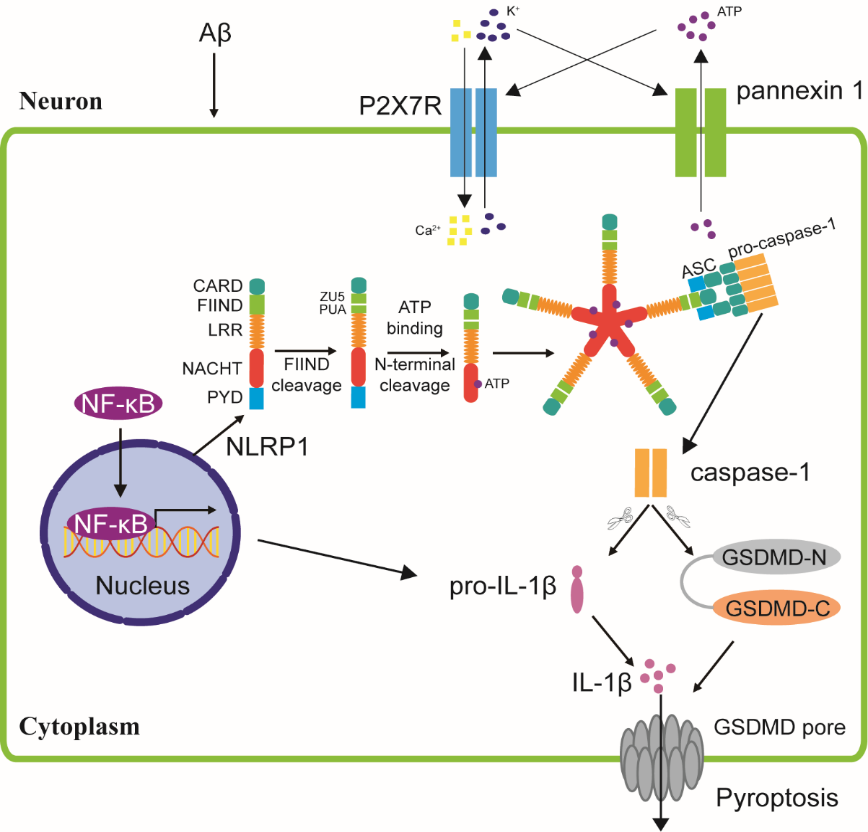
图3 NLRP1炎症小体活化及其介导的细胞焦亡(图源:Hu et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
NLRP3和NLRP1活化分别介导小胶质细胞焦亡和神经元细胞焦亡。同时,还有研究表明,NLRP3炎症小体活化可介导神经元细胞焦亡。小胶质细胞和神经元可以通过分泌外泌体相互交流,外泌体将细胞内成分输送到细胞外空间,然后通过内吞作用进入对方[10]。因此,淀粉样蛋白β诱导的NLRP3介导的小胶质细胞焦亡最终导致神经元焦亡。
NLRP3或NLRP1炎症小体激活诱导细胞焦亡,进一步导致阿尔茨海默病神经元的死亡。因此,靶向NLRP3和/或NLRP1炎症小体可能是一种前景光明的阿尔茨海默病治疗策略。该论文概括了NLRP3的几种典型小分子抑制剂(包括MCC950、CY-09、OLT1177和JC-124)(图4A-D)和抑制性微小RNAs(microRNA-22和microRNA-212-3p)、NLRP1的内源性抑制蛋白二肽基肽酶(DPP8/DPP9)和抑制性微小RNAs(microRNA-181c-5p)。更为重要的是,贾金婧等还总结了几种天然活性成分,包括白藜芦醇、姜黄素、五味子素和人参皂苷Rg1(图4E-H)。它们表现出对NLRP3和NLRP1炎症小体活化的双重抑制作用。另外,2种炎症小体的共同组分caspase-1的选择性抑制剂童谣可以起到双重抑制作用。
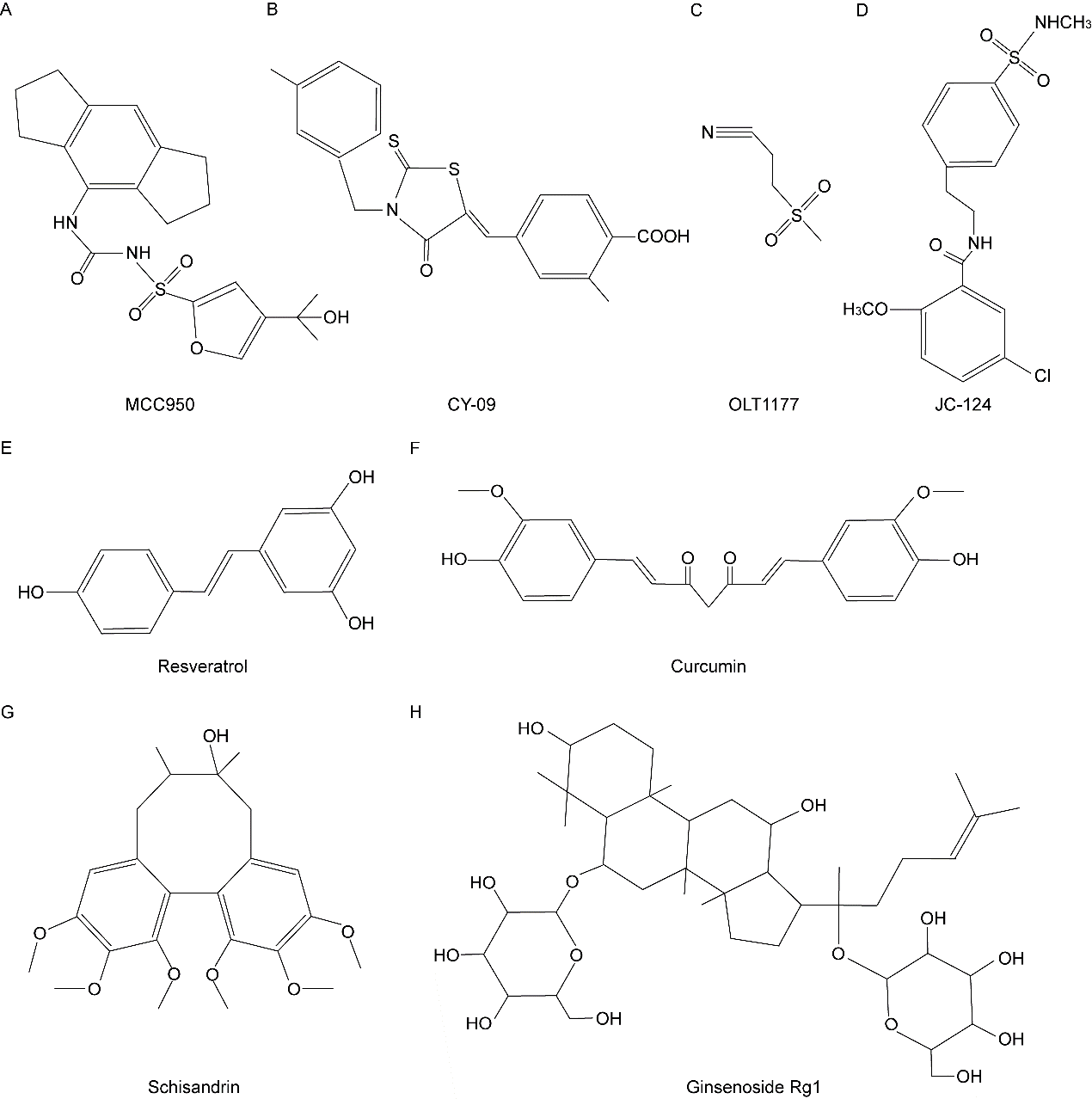
图4 NLRP3和NLRP1炎症小体抑制剂的化学结构(图源:Hu et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
综上所述,神经炎症与阿尔茨海默病的发生和发展密切相关。小胶质细胞中NLRP3炎症小体和阿尔茨海默病大脑神经元中NLRP1炎症小体的激活将caspase-1前体切割为活性caspase-1,后者将剪切GSDMD产生GSDMD-N,形成跨膜孔并诱导细胞焦亡。Caspase-1促使白细胞介素18前体和白细胞介素1β前体成熟为白细胞介素18和白细胞介素1β,这些细胞炎症因子从GSDMD-N孔分泌到细胞外空间,加重焦亡细胞的死亡。在过去的20年里,设计或鉴定了几种靶向NLRP3或NLRP1炎症小体和caspase-1的小分子抑制剂、微小RNA和天然活性成分,并在体外和体内探索中显示出显著的阿尔茨海默病治疗效果。因此,靶向NLRP3或NLRP1炎症小体介导的细胞焦亡是一种前景光明的阿尔茨海默病治疗策略。
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.391311
参考文献
[1] Jia JJ, Zeng XS, Song XQ, et al. Diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer's disease: the protection of epigallocatechin-3-gallate in streptozotocin injection-induced models. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:834.
[2] Feng W, Zhang Y, Wang Z, et al. Microglia prevent beta-amyloid plaque formation in the early stage of an Alzheimer's disease mouse model with suppression of glymphatic clearance. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2020;12(1):125.
[3] Kabir MT, Uddin MS, Zaman S, et al. Molecular mechanisms of metal toxicity in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2021;58(1):1-20.
[4] Malik A, Kanneganti TD. Inflammasome activation and assembly at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2017;130(23):3955-3963.
[5] Yang F, Bettadapura SN, Smeltzer MS, et al. Pyroptosis and pyroptosis-inducing cancer drugs. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022;43(10):2462-2473.
[6] Liang T, Zhang Y, Wu S, et al. The role of NLRP3 inflammasome in Alzheimer's disease and potential therapeutic targets. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:845185.
[7] Gurung P, Anand PK, Malireddi RK, et al. FADD and caspase-8 mediate priming and activation of the canonical and noncanonical Nlrp3 inflammasomes. J Immunol. 2014;192(4):1835-1846.
[8] Swanson KV, Deng M, Ting JP. The NLRP3 inflammasome: molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat Rev Immunol. 2019;19(8):477-489.
[9] Yap JKY, Pickard BS, Chan EWL, et al. The role of neuronal NLRP1 inflammasome in Alzheimer's disease: bringing neurons into the neuroinflammation game. Mol Neurobiol. 2019;56(11):7741-7753.
[10] Mattingly J, Li Y, Bihl JC, et al. The promise of exosome applications in treating central nervous system diseases. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2021;27(12):1437-1445.



