中国神经再生研究(英文版) ›› 2025, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (7): 1883-1899.doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-00048
脂质体治疗创伤和非创伤性中枢神经系统疾病的所面临的药物稳定性、靶向效率和安全性挑战
Liposomes as versatile agents for the management of traumatic and nontraumatic central nervous system disorders: drug stability, targeting efficiency, and safety
Mingyu Zhang, Chunyu Xiang, Renrui Niu, Xiaodong He, Wenqi Luo* , Wanguo Liu* , Rui Gu*
- Department of Orthopedic Surgery, China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, Jilin Province, China
摘要:
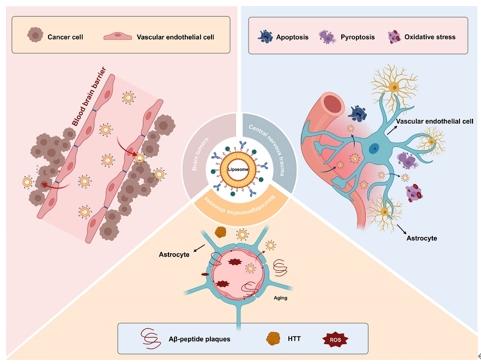
用于治疗神经系统疾病的多种基于纳米颗粒的药物递送系统已被广泛研究。然而,缺乏穿越血脑屏障的能力阻碍了这些系统的临床转化效果。脂质体是由脂质双层组成的纳米颗粒,可有效地封装药物,并通过其靶向性和渗透性改善药物在血脑屏障和脑组织中的递送,因而具有治疗创伤性和非创伤性中枢神经系统疾病的可能。为此,文章首先回顾了脂质体的常见表征和制备方法,包括薄膜水化、逆向蒸发、溶剂注入、洗涤剂去除以及微流体技术;随后全面讨论了目前脂质体在阿尔茨海默病、帕金森病、亨廷顿舞蹈症、肌萎缩侧索硬化、创伤性脑损伤、脊髓损伤和脑肿瘤等中枢神经系统疾病的应用;最后基于大多数脂质体相关研究仍处于实验室阶段,尚未进入临床试验,其作为药物递送系统在临床实践中的应用仍然面临着药物稳定性、靶向效率和安全性等挑战,进而提出有关脂质体的发展策略以进一步促进其在神经疾病研究中的发展。
https://orcid.org/0009-0001-4652-5561 (Rui Gu); https://orcid.org/0009-0004-8053-9934 (Wanguo Liu);
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4441-9095 (Wenqi Luo)