中国神经再生研究(英文版) ›› 2025, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (8): 2231-2244.doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-00119
CCL2/CCR2通路成为脊髓损伤治疗靶点和调控方式的可能性
C–C motif chemokine ligand 2/C–C motif chemokine receptor 2 pathway as a therapeutic target and regulatory mechanism for spinal cord injury
Xiangzi Wang1, #, Xiaofei Niu2 #, Yingkai Wang1 , Yang Liu1 , Cheng Yang3, *, Xuyi Chen3, *, Zhongquan Qi1, 4, *
- 1 School of Medicine, Guangxi University, Nanning, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2 Graduate School of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin, China; 3 Characteristic Medical Center of People’s Armed Police Forces, Tianjin, China; 4 Fujian Maternity and Child Health Hospital, Fuzhou, Fujian Province, China
摘要:
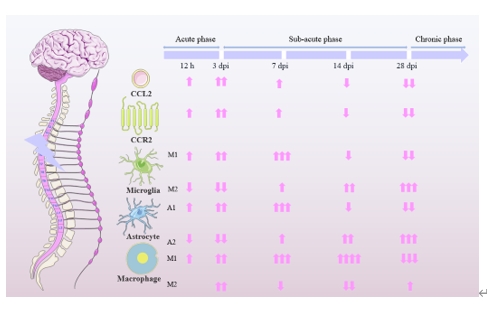
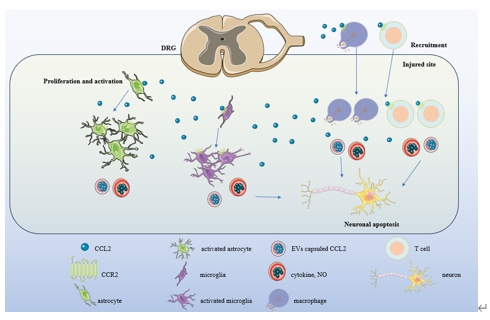
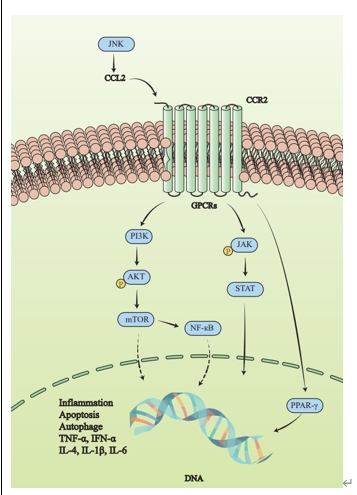
脊髓损伤是一种不可逆的中枢神经系统损伤,其特征是再生能力有限和继发性炎症损伤。CCL2/CCR2轴的表达在脊髓损伤前后存在显著差异。最近有研究认为,CCL2/CCR2轴与脊髓损伤后继发性炎症反应和免疫细胞募集密切相关,这表明CCL2/CCR2轴可能是脊髓损伤的一个新的治疗靶点和调节节点。此次综述总结了CCL2/CCR2轴与脊髓损伤再生修复机制,概括了脊髓损伤与CCL2/CCR2轴相关的上下游炎症相关信号通路,重点阐述了针对CCL2/CCR2通路的治疗策略与最新拮抗药物的研究进展和有关CCL2/CCR2轴作为新治疗靶点的调控方式以及靶向药物的开发,这将为未来脊髓损伤治疗提供了新的思路和治疗策略。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0420-8349 (Xuyi Chen); Zhongquan, Qi, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7210-4955.
 #br#
#br#
 #br#
#br#