中国神经再生研究(英文版) ›› 2024, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (9): 1890-1898.doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.390964
小胶质细胞NLRP3炎症小体介导抑郁神经炎症及其治疗策略
Microglial NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuroinflammation and therapeutic strategies in depression
Qiuqin Han1, *, #, Wenhui Li1, #, Peiqing Chen1, Lijuan Wang1, Xiwen Bao1, Renyan Huang2, Guobin Liu2, *, Xiaorong Chen3, *
- 1Department of Scientific Research, Shanghai University of Medicine & Health Sciences Affiliated Zhoupu Hospital, Shanghai, China; 2Department of Traditional Chinese Vascular Surgery, Shuguang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China; 3Department of Physiology, Laboratory of Neurodegenerative Diseases, Changzhi Medical College, Changzhi, Shanxi Province, China
摘要:
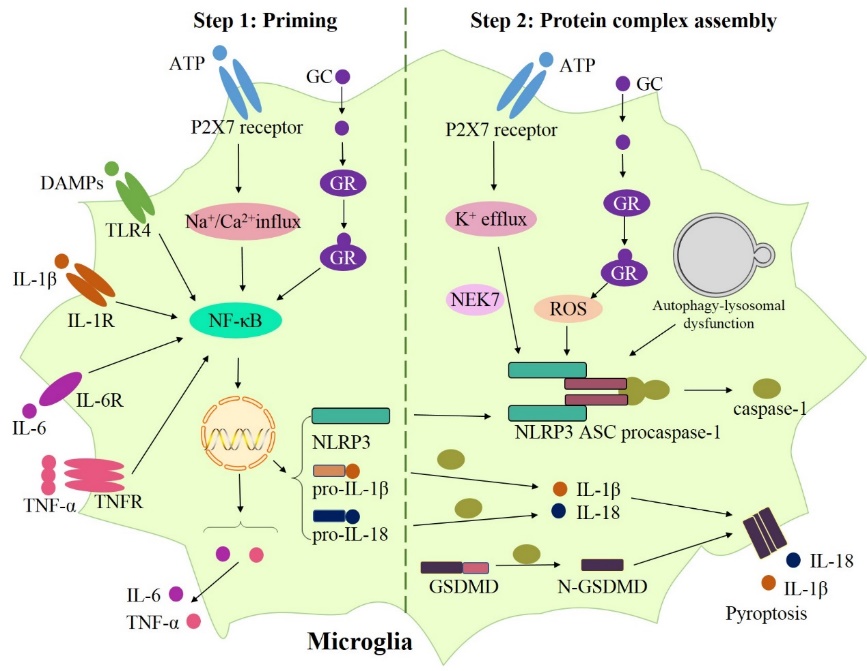
有证据表明,炎症和抑郁之间存在双向关系。由于NLRP3炎症小体的激活与多种神经系统疾病的发病机制密切相关,且在重度抑郁患者中,NLRP3炎症小体显著高表达。因此,了解NLRP3炎症小体介导的神经炎症在抑郁发病机制中的作用将有利于探索未来的治疗策略。此次综述旨在阐明抑郁中导致NLRP3炎症小体激活的机制,并深入了解针对NLRP3炎性小体的治疗策略。此外,文章还概括了针对NLRP3炎症小体的各种治疗策略,包括NLRP3炎性通路抑制剂、天然化合物和其他化合物以及非药物疗法。这些方法在抑郁治疗方面取得了显著效果。最后总结了有关抑郁临床试验中NLRP3炎症小体抑制剂的应用。虽然目前关于NLRP3炎症小体抑制剂在抑郁治疗的临床试验还很少,但该领域的研究已经引起了广泛关注,这为抑郁治疗带来了新希望。因此有必要确定这些方法治疗抑郁的有效性和安全性,这将为临床抑郁治疗开辟新的道路。
https://orcid.org/0009-0008-8311-4527 (Xiaorong Chen); https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3283-4275 (Guobin Liu); https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7060-1459 (Qiuqin Han)