NRR:天津医科大学雷平团队提出高表达miR-124-3p的小胶质细胞外泌体可减少创伤性脑损伤后神经元损伤
撰文:王艳,殷振宇
创伤性脑损伤是造成全球疾病负担的重要原因。全世界每年报告的创伤性脑损伤病例数超过5000万,据估计,创伤性脑损伤每年给全球经济造成的损失约为4000亿美元。海马体神经细胞凋亡是脑损伤后患者发生认知功能障碍的主要原因。在不同的应激条件下,蛋白质平衡状态,特别是内质网成分的功能障碍,导致未折叠或错误折叠的蛋白质在内质网腔内积聚,引发“内质网应激”。有研究表明,内质网应激可参与创伤性脑损伤后继发性神经功能损伤的病理过程。小胶质细胞及其分泌的外泌体在脑损伤后神经元损伤及修复的过程发挥至关重要的作用,已有研究表明高表达miR-124-3p的小胶质细胞外泌体可改善创伤性脑损伤后的认知功能障碍,但其详细机制仍不明确。
最近,来自中国天津医科大学雷平团队在《中国神经再生研究(英文版)》(Neural Regeneration Research)上发表了题为“Exosomes derived from microglia overexpressing miR- 124-3p alleviate neuronal endoplasmic reticulum stress damage after repetitive mild traumatic brain injury”的研究。实验发现,高表达miR-124-3p的小胶质细胞可通过其分泌的外泌体抑制创伤性脑损伤诱导的神经元内质网应激,进而减少神经元的凋亡。进一步研究证实,高表达miR-124-3p的小胶质细胞外泌体可能是通过靶向IRE1α从而调控IRE1α/XBP1s信号通路来实现的。这一研究启示,内质网应激进而参与创伤性脑损伤后神经元凋亡的调控,而通过基因编辑或者工程化改造的外泌体可能在未来创伤性脑损伤继发认知功能障碍的治疗中起到关键作用。
小胶质细胞及其分泌的外泌体在创伤性脑损伤的病理进程中发挥至关重要的作用[1-3],雷平等在其前期研究[4]的基础上提出,高表达miR-124-3p的小胶质细胞外泌体改善创伤性脑损伤神经认知功能的作用可能是通过调控神经元内质网应激实现的。实验首先使用体外培养的HT22海马神经元进行划痕损伤以模拟体内创伤性脑损伤,同时给予内质网应激抑制剂TUDCA进行干预,结果发现,划痕损伤后,与内质网应激相关的一系列蛋白GRP78,p-IRE1α,XBP1s以及CHOP的表达水平发生了明显的改变;而给予内质网应激抑制剂TUDCA后,上述内质网应激相关蛋白的表达和凋亡相关蛋白Caspase3及Caspase12的表达明显减少。这表明内质网应激参与创伤性脑损伤后神经元凋亡的病理进程(图1)。

图1抑制内质网应激可以改善神经元划痕引起的细胞凋亡(图源:Wang et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
雷平等在HT22神经元细胞体外划痕损伤模型建立后,通过Transwell使其与高表达miR-124-3p的BV2小胶质细胞共培养,并通过使用外泌体分泌抑制剂GW4869进行干预,结果证实小胶质细胞来源的高表达miR-124-3p的外泌体可改善划痕损伤神经元的凋亡和内质网应激,阻断外泌体的释放后这种作用减弱(图2)。

图2高表达miR-124-3p的小胶质细胞外泌体可抑制划痕损伤神经元的内质网应激和细胞凋亡(图源:Wang et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
在接下来的实验中,雷平等使用荧光素酶报告实验验证了miR-124-3p与内质网应激相关蛋白IRE1α的特异性结合位点,同时通过IRE1α功能挽救实验证实, miR-124-3p可以通过靶向IRE1α降低其表达,从而抑制损伤神经元的内质网应激(图3和4)。
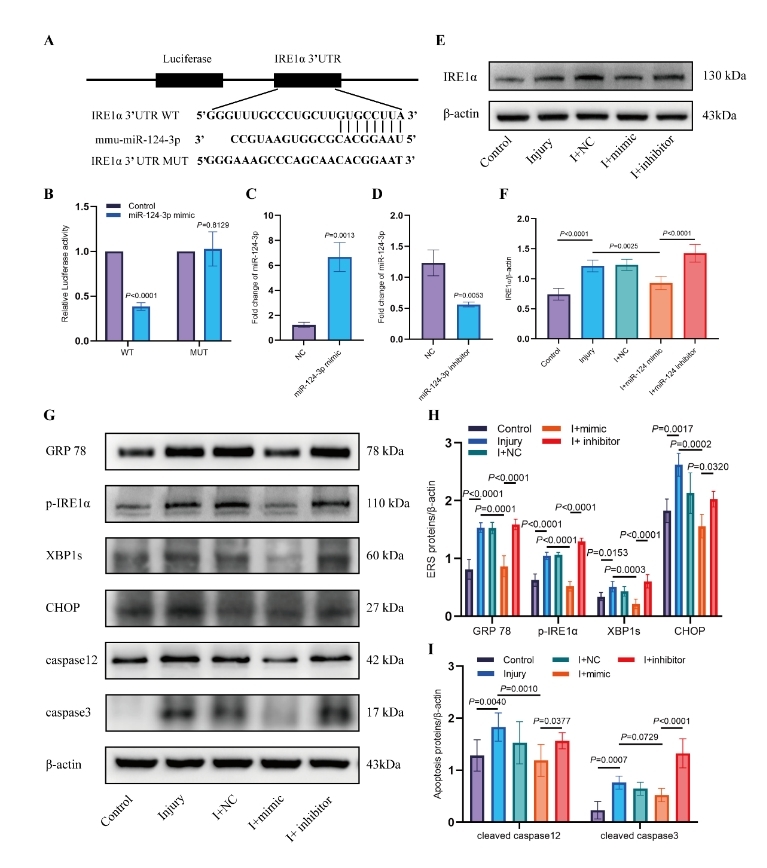
图3 miR-124-3p靶基因IRE1α荧光素酶报告实验(图源:Wang et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)

图4 靶基因IRE1α功能挽救实验(图源:Wang et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
最后雷平等在体内重复性轻度创伤性脑损伤模型鼠中通过鼻腔给药高表达miR-124-3p的小胶质细胞外泌体,证实了其改善内神经元内质网应激和减少细胞凋亡的作用(图5)。
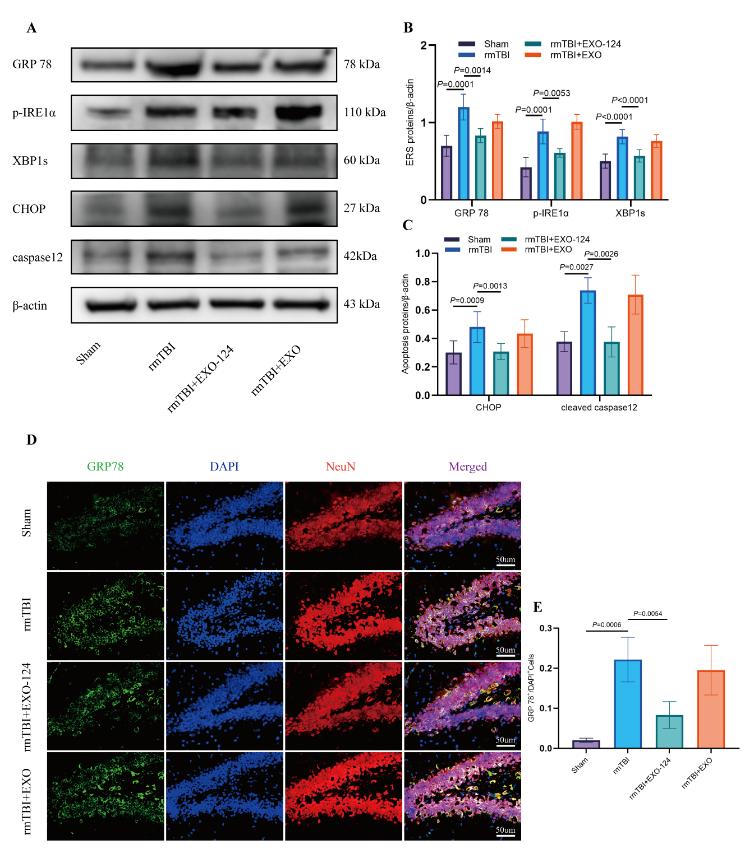
图5高表达miR-124-3p的小胶质细胞外泌体抑制神经元内质网应激及凋亡的体内实验验证(图源:Wang et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
综上,内质网应激参与了创伤性脑损伤中神经元凋亡的病理进程。作者的研究,高表达miR-124-3p的小胶质细胞通过其分泌的外泌体抑制创伤性脑损伤诱导的神经元内质网应激,减轻细胞凋亡。miR-124-3p通过靶向IRE1α调控IRE1α/XBP1s是其具体的作用通路(图6)。鼻腔给予重复性轻度创伤性脑损伤小鼠高表达miR-124-3p的小胶质细胞外泌体治疗,初步证实高表达miR-124-3p的小胶质细胞外泌体可抑制重复性轻度创伤性脑损伤后小鼠脑组织神经元内质网应激并减少神经元细胞凋亡,减轻神经损伤及改善认知功能障碍,从而为重复性轻度创伤性脑损伤所致远期认知功能障碍的治疗策略提供了相应的理论基础。
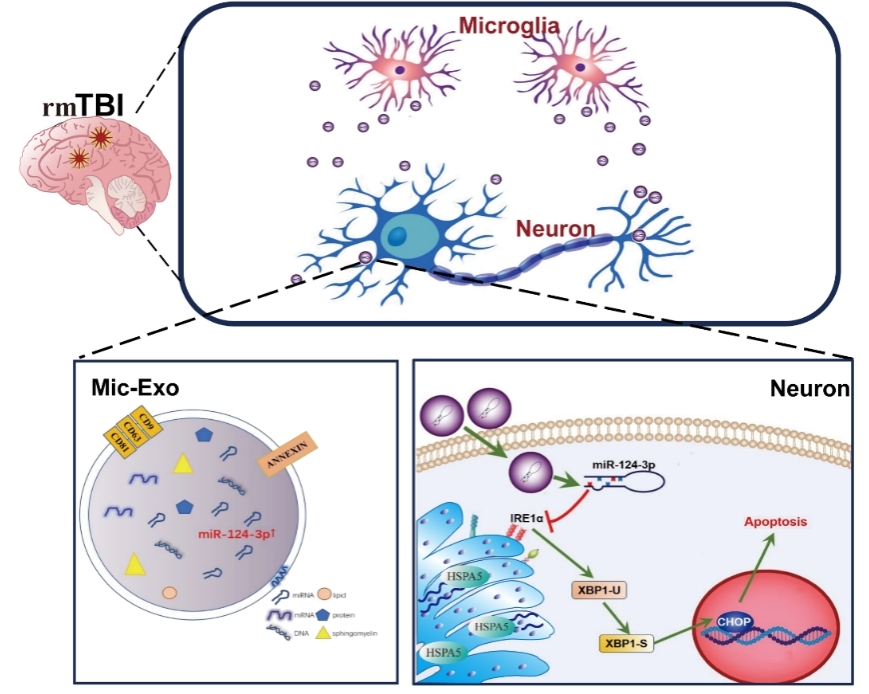
图6高表达miR-124-3p的小胶质细胞外泌体抑制神经元内质网应激及凋亡的机制示意图(图源:Wang et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
同时,研究也存在一定的局限性,主要研究部分集中于体外的创伤性脑损伤神经元损伤模型,虽然机制探索比较详细,但是体内的动物模型只做了初步的蛋白表达检测,尚未进行认知行为学检测及体内内质网应激相关靶蛋白的干预及验证。
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.391189
参考文献
[1] Manjally AV, Tay TL. Attack of the clones: microglia in health and disease. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022;16:831747.
[2] Ritzel RM, Li Y, Jiao Y, et al. Brain injury accelerates the onset of a reversible age-related microglial phenotype associated with inflammatory neurodegeneration. Sci Adv. 2023;9(10):eadd1101.
[3] Wang B, Xing D, Zhu Y, et al. The state of exosomes research: a global visualized analysis. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:1495130.
[4] Ge X, Guo M, Hu T, et al. Increased microglial exosomal miR-124-3p alleviates neurodegeneration and improves cognitive outcome after rmTBI. Mol Ther. 2020;28(2):503-522.

通讯作者:雷平教授,博士生导师。天津市老年医学研究所所长,中枢神经损伤修复与再生教育部重点实验室主任。国家“百千万人才”,人社部“有突出贡献中青年专家”,国务院政府特殊津贴专家,天津市教委“十三五”学科领军人才,天津市“131”创新型人才团队第一层次人才。任中国医师协会老年医学科医师分会副会长、中华医学会老年医学分会全国委员、天津市医师协会老年医学科医师分会会长、天津市医学会老年医学分会副主任委员,长期聚焦慢性颅脑创伤致认知障碍的作用机制及潜在干预策略,先后主持国家自然科学基金等国家级、省部级项目十余项。






