NRR:昆医大杨新旺团队发现一种可促进脊髓损伤后功能恢复的新型多肽
撰文:李姗姗、杨新旺
脊髓损伤是一种严重中枢神经系统损伤,具有高发病率、高致残率和高死亡率的特征。由于中枢神经系统再生能力非常有限,目前对脊髓损伤有效的治疗方法很少,因此寻找促脊髓损伤后结构和功能恢复的药物先导分子具有重要的意义。
多肽药物因其高选择性、高生物活性和低抗原性而越来越受到药物研究和开发的关注。来自两栖动物的小分子多肽是该类多肽的优良天然来源。有多肽被报道可显著地促损伤组织修复和再生。虽然两栖动物的脊髓再生能力很强,但很少有研究探讨两栖动物脊髓来源的多肽对脊髓损伤的影响。
来自中国昆明医科大学基础医学院杨新旺博士团队长期从事两栖动物来源的多肽药物研究,近期,该团队在《中国神经再生研究(英文版)》(Neural Regeneration Research)上发表了题为“A new peptide, VD11, promotes structural and functional recovery after spinal cord injury”的研究。杨新旺等从中国特有两栖动物花臭蛙脊髓中成功分离鉴定一种新型多肽—VD11,并发现其在体内外均具有显著的神经保护作用。细胞实验表明,VD11可促进小胶质细胞神经生长因子和脑源性神经营养因子的分泌,促进缺氧损伤后PC12细胞的增殖和突触延长。动物实验也表明,椎管内注射VD11可明显促进脊髓损伤大鼠运动功能的恢复,减轻其病理损伤,并促进轴突的再生。这一现象可能与AMPK和AKT信号通路的激活相关。该研究分离出首个来源于两栖动物脊髓可促进脊髓损伤修复的肽,这为未来的药物研究提出了一种新的可能。
杨新旺等在花臭蛙脊髓中发现了一种编码多肽前体的cDNA序列,其是由221 bp的mRNA编码的含有58个氨基酸残基的前体,成熟序列为VDELWPPWLPC。经NCBI BLAST搜索,没有发现相同的多肽,因此被认定为一种全新的多肽,将其命名为VD11(图1)。
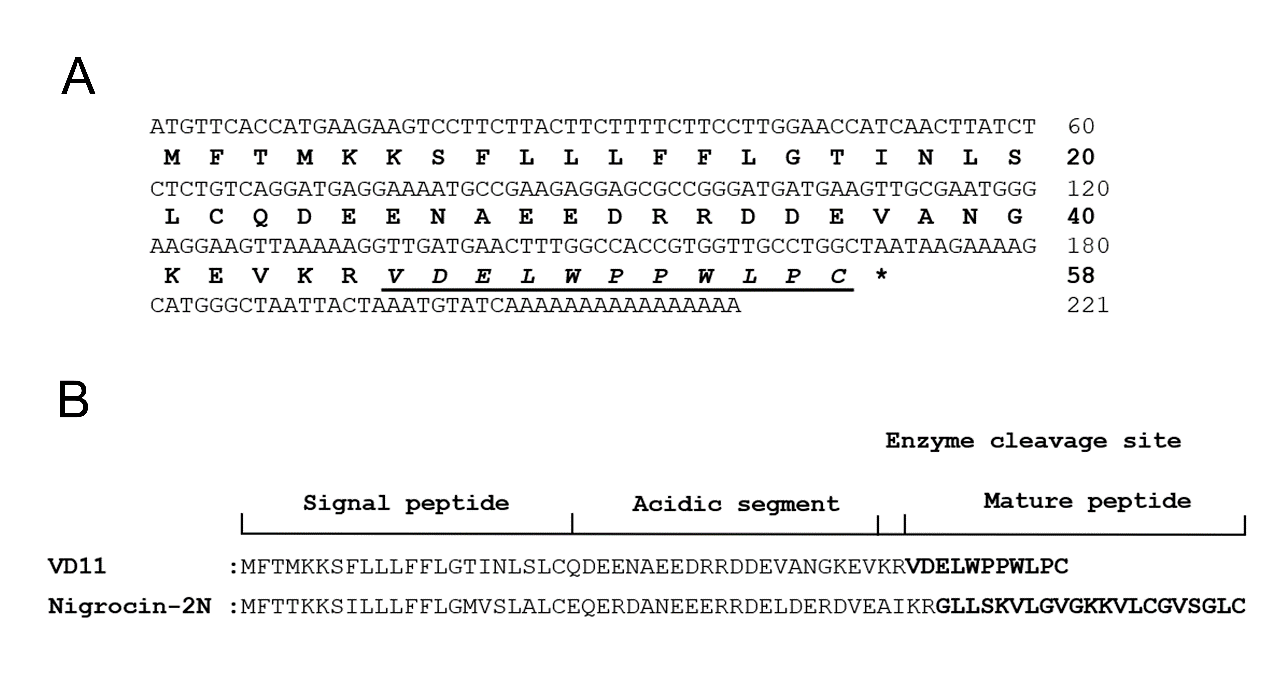
图1 VD11的多肽序列(图源:Li et al., Neural Regen Res, 2023)
神经生长因子和脑源性神经营养因子在轴突再生中均起重要作用[1],因此首先检测了VD11对神经生长因子和脑源性神经营养因子的转录和表达的影响,可见VD11在体内外均能促进神经生长因子和脑源性神经营养因子的分泌(图2)。
 #br#
#br#
图2 VD11在体内外均可促进神经生长因子和脑源性神经营养因子的分泌(图源:Li et al., Neural Regen Res, 2023)
为进一步确定VD11的神经保护作用,采用氧糖剥夺复氧模型模拟脊髓损伤后继发的缺血缺氧再灌注损伤,并检测VD11对正常PC12细胞及细胞缺氧损伤后的细胞活性的影响。结果显示,低浓度(1-100 nM)VD11对正常和氧糖剥夺复氧细胞的活性均有显著的促进作用,且这一作用呈浓度依赖效应。此外,氧糖剥夺复氧后48 h,细胞数量和轴突长度均显著减少,而VD11 (100 nM)干预则明显改善细胞数量和轴突长度(图3)。表明VD11能促进缺氧损伤PC12细胞的增殖和轴突延长。
 #br#
#br#
图3 VD11能促进PC12细胞增殖和轴突再生(图源:Li et al., Neural Regen Res, 2023)
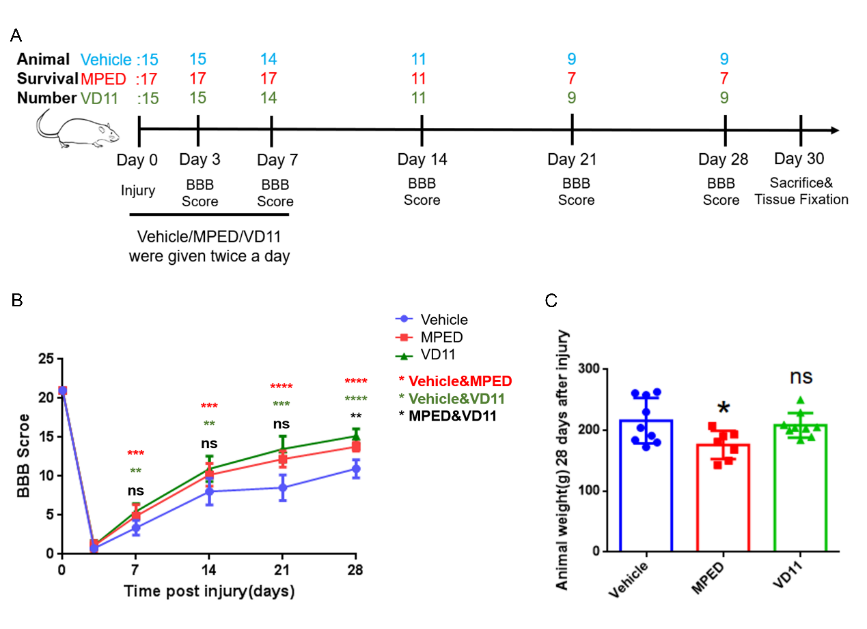
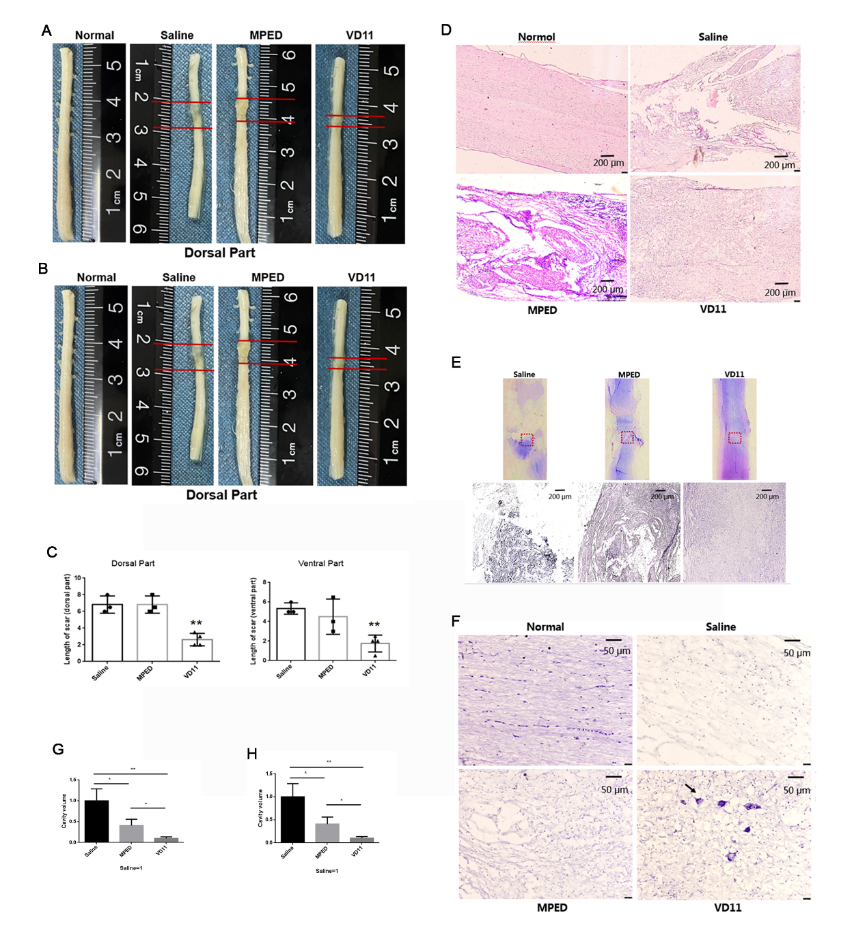
甲泼尼龙可通过抑制免疫系统,降低炎症反应来改善脊髓损伤的预后[2]。然而,长期大量使用甲泼尼龙则会带来严重并发症,包括胃出血、败血症、肺炎、急性皮质类固醇肌病以及伤口感染等[3]。动物实验发现,脊髓损伤后28d时,与甲泼尼龙相比,VD11对运动功能的恢复效果更好,且副作用更小。值得注意的是而在研究使用的甲泼尼龙的剂量是VD11的300倍,这说明VD11在低剂量下就存在更优越的活性(图4)。随后的组织学检查结果也表明VD11可减少组织瘢痕和空洞(图5)。
 #br#
#br#
图4 VD11能促进脊髓损伤大鼠后肢功能的恢复(图源:Li et al., Neural Regen Res, 2023)
 #br#
#br#
图5 VD11能促进脊髓损伤大鼠脊髓组织结构的修复(图源:Li et al., Neural Regen Res, 2023)
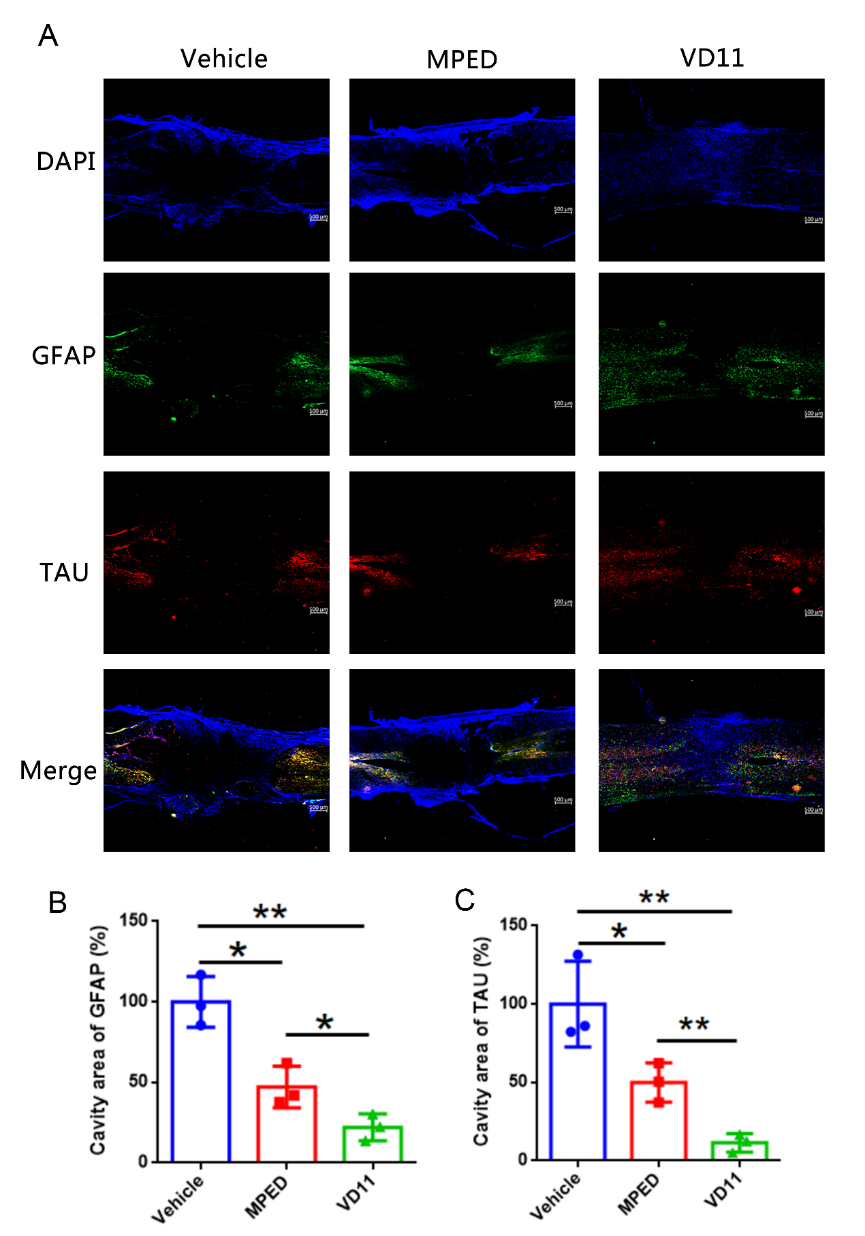
为进一步确定VD11是否有益于损伤后的神经组织的存活或再生,杨新旺等对大鼠损伤脊髓组织进行了免疫荧光分析。结果显示,VD11组星形胶质细胞的增殖和轴突再生比溶剂组和甲泼尼龙组更显著,表明VD11可减轻脊髓损伤后神经损伤,并促进轴突再生。形成瘢痕的星形胶质细胞长期以来一直被认为是中枢神经系统轴突再生失败的主要原因[4],但目前这一观点受到了质疑[5]。多项研究表明,适当的生长因子或基因激活刺激中枢神经系统损伤后,成熟的中枢神经系统轴突会沿星形胶质细胞再生[6]。因此,星形胶质细胞瘢痕可能有助于而不是阻碍轴突再生[7]。由此可见,VD11促进轴突再生的能力可能与其能促进星形胶质细胞再生有关。此外,VD11还能有效减少瘢痕的形成(图6)。
 #br#
#br#
图6 免疫荧光显示VD11能促进脊髓损伤后神经组织的再生(图源:Li et al., Neural Regen Res, 2023)
最后,杨新旺等进一步探索了VD11可能的作用机制。根据脊髓损伤后大鼠的脊髓组织RNA测序结果,检测了与神经恢复相关的AMPK和AKT的激活情况。前者是一种丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶,可在细胞中起能量传感器的作用[8]。AMPK信号通路与能量供应和氧化应激有关,这两者都可以显著破坏代谢过程[9]。脊髓损伤后缺血缺氧可导致活性氧明显升高[10]。AMPK磷酸化在脊髓损伤后的轴突修复中起着积极的作用[11]。与氧糖剥夺复氧组相比,VD11可增加磷酸化AMPK水平,而Akt可在多种细胞代谢中起关键作用。最近,有多项研究表明,AKT在脊髓损伤后的防止神经细胞凋亡和抑制炎症方面起重要作用[12-14]。综上VD11可能通过激活AMPK和AKT通路来保护PC12细胞免受氧糖剥夺复氧模型损伤(图7)。
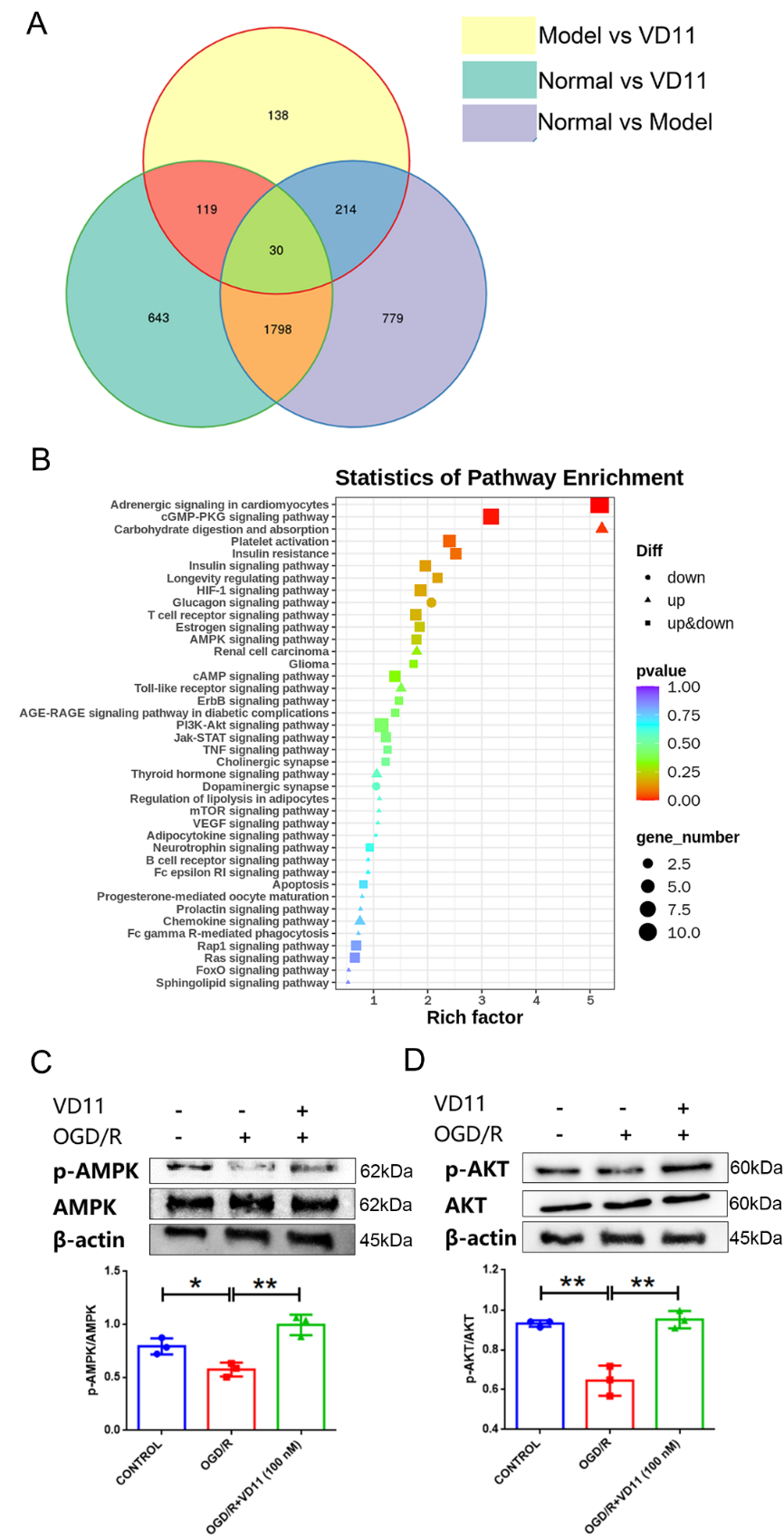 #br#
#br#
图7 VD11可激活氧糖剥夺复氧后AMPK和AKT通路(图源:Li et al., Neural Regen Res, 2023)
总之,研究发现了一种新型的两栖动物来源的肽VD11。在体外研究中,VD11可促进小胶质细胞神经生长因子和脑源性神经营养因子的分泌,促进缺氧损伤后PC12细胞的增殖和延长。在体内研究中,VD11可明显改善脊髓损伤大鼠的运动功能,减轻神经损伤,促进轴突再生,其机制可能与激活AMPK和AKT信号通路有关。这一研究结果为脊髓损伤药物探索开括了思路。
文章链接:https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.369119
参考文献
[1] Li L, Pu Q, Hintze M, et al. BDNF and NGF signals originating from sensory ganglia promote cranial motor axon growth. Exp Brain Res. 2020;238(1):111-119.
[2] Bracken MB, Shepard MJ, Collins WF, Jr., et al. Methylprednisolone or naloxone treatment after acute spinal cord injury: 1-year follow-up data. Results of the second National Acute Spinal Cord Injury Study. J Neurosurg. 1992;76(1):23-31.
[3] Xu J, Fan G, Chen S, et al. Methylprednisolone inhibition of TNF-alpha expression and NF-kB activation after spinal cord injury in rats. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1998;59(2):135-142.
[4] Silver J, Miller JH. Regeneration beyond the glial scar. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004;5(2):146-156.
[5] Wu D, Klaw MC, Connors T, et al. Expressing constitutively active rheb in adult neurons after a complete spinal cord injury enhances axonal regeneration beyond a chondroitinase-treated glial scar. J Neurosci. 2015;35(31):11068-11080.
[6] Kawaja MD, Gage FH. Reactive astrocytes are substrates for the growth of adult CNS axons in the presence of elevated levels of nerve growth factor. Neuron. 1991;7(6):1019-1030.
[7] Anderson MA, Burda JE, Ren Y, et al. Astrocyte scar formation aids central nervous system axon regeneration. Nature. 2016;532(7598):195-200.
[8] Tian L, Cao W, Yue R, et al. Pretreatment with Tilianin improves mitochondrial energy metabolism and oxidative stress in rats with myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1 alpha signaling pathway. J Pharmacol Sci. 2019;139(4):352-360.
[9] De Oliveira MR, De Souza ICC, Brasil FB. Promotion of mitochondrial protection by emodin in methylglyoxal-treated human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells: involvement of the AMPK/Nrf2/HO-1 axis. Neurotox Res. 2021;39(2):292-304.
[10] Wang H, Zheng Z, Han W, et al. Metformin promotes axon regeneration after spinal cord injury through inhibiting oxidative stress and stabilizing microtubule. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:9741369.
[11] Hu H, Xia N, Lin J, et al. Zinc Regulates glucose metabolism of the spinal cord and neurons and promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury through the AMPK signaling pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:4331625.
[12] Chen J, Wang Z, Zheng Z, et al. Neuron and microglia/macrophage-derived FGF10 activate neuronal FGFR2/PI3K/Akt signaling and inhibit microglia/macrophages TLR4/NF-κB-dependent neuroinflammation to improve functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8(10):e3090.
[13] Cai J, Qi Z, Tang W, et al. The role of the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway in bFGF/PDGF composite hydrogel promoting the repair of spinal cord injuries. Ann Ital Chir. 2021;92:92-97.
[14] He X, Li Y, Deng B, et al. The PI3K/AKT signalling pathway in inflammation, cell death and glial scar formation after traumatic spinal cord injury: Mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Cell Prolif. 2022;55(9):e13275.
杨新旺,昆明医科大学基础医学院,副院长,副教授,硕士生导师,入选首批云南省高层次人才培养支持计划——万人计划青年拔尖人才,昆明市中青年学术技术带头人。杨新旺博士立足于中国西南独特的资源优势,以“活性肽的发现、结构与功能、机制”为切入点,以临床需求为导向,利用基础医学、再生医学、皮肤病学、药学、生物学等多学科交叉技术手段与方法,重点关注“动物适应生境的生存策略解析”、“基于活性肽的新型促皮肤创面愈合干预策略及机制”、“高原性光损伤皮肤保护活性肽的发现、结构、功能与机制”、“抗高尿酸/痛风活性肽的结构与功能”、“神经系统损伤机制与肽类分子干预策略”等研究方向;先后主持国家自然科学基金、云南省科技厅—昆明医科大学联合专项重点项目、云南省应用基础研究面上项目、云南省教育厅科学研究基金等科研项目;以通讯/第一作者身份正式发表或接收SCI 研究论文45篇,代表性研究工作发表于国际著名期刊如PNAS、NPG Asia Materials、Journal of Biological Chemistry、Journal of Proteome Research(封面文章)、ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces、Pharmacological Research、Journal of Nanobiotechnology、Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry、Burns & Trauma、Materials & Design、Food & Function、Journal of Photochemistry & Photobiology, B: Biology等。获国家发明专利授权18项、实用新型专利授权1项,开展了12项发明专利技术转移工作。

 #br#
#br#
 #br#
#br#
 #br#
#br#
 #br#
#br#
 #br#
#br#
 #br#
#br#