中国神经再生研究(英文版) ›› 2024, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (4): 811-817.doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.382225
利用体内成像解读神经元对损伤的反应:基于脊髓损伤治疗的紧迫性
In vivo imaging of the neuronal response to spinal cord injury: a narrative review
Junhao Deng1, 2, 3, #, Chang Sun1, 2, 4, #, Ying Zheng5, Jianpeng Gao1, 2, Xiang Cui1, 2, Yu Wang6, 7, Licheng Zhang1, 2, *, Peifu Tang1, 2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, The Fourth Medical Center of Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, China; 2National Clinical Research Center for Orthopedics, Sports Medicine and Rehabilitation, Beijing, China; 3School of Life Sciences, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China; 4Department of Orthopedics, Air Force Medical Center, PLA, Beijing, China; 5Medical School of Chinese PLA, Beijing, China; 6Institute of Orthopedics, The First Medical Center, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, China; 7Key Lab of Regenerative Medicine in Orthopedics, Key Laboratory of Musculoskeletal Trauma and War Injuries PLA, Beijing, China
摘要:
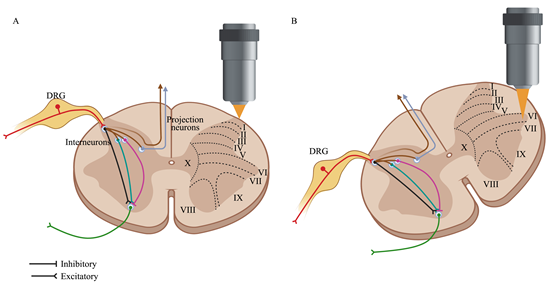
解读脊髓损伤后的神经元反应对于探索脊髓损伤治疗的潜在策略具有重要的意义。然而,目前仍缺乏探索脊髓损伤后神经元对损伤的反应,其部分原因是缺乏合适的工具。传统的电生理学在观察兴奋细胞生物电活动时存在攻击性和侵入性,且无法识别细胞类型或精确的空间位置,也无法进行长期观察。目前,新出现的体内成像和适当标记方法为观察中枢神经系统正常或损伤状态下神经元的动态过程提供了新的途径。此次综述首先对小鼠脊髓进行体内成像,重点是观察脊髓神经元的最新手段进行回顾,分析了脊髓感觉及运动神经元对脊髓损伤的动态生物学反应,总结对比了作为探索脊髓损伤神经元反应的研究手段,并阐明体内成像相较传统神经科学检查的优势,最后还明确了脊髓神经元成像的接下来所面临的挑战和可能的解决方案。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1024-4098 (Licheng Zhang)

 #br#
#br#