中国神经再生研究(英文版) ›› 2025, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (1): 116-129.doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-23-01292
非编码RNA与急性缺血性脑卒中:从中枢到外周
Non-coding RNAs in acute ischemic stroke: from brain to periphery
Shuo Li1, #, Zhaohan Xu1, #, Shiyao Zhang2, Huiling Sun3, Xiaodan Qin3, Lin Zhu1, Teng Jiang1, Junshan Zhou1, Fuling Yan2, *, Qiwen Deng1, *
- 1Department of Neurology, Nanjing First Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Neurology, Zhongda Hospital, School of Medicine, Southeast University, Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, China; 3General Clinical Research Center, Nanjing First Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
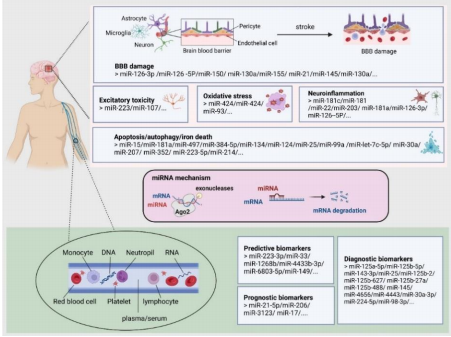
急性缺血性脑卒中是一种发病率高、死亡率高、致残率高的临床急症。有关急性缺血性脑卒中的准确预测、诊断和预后生物标志物及有效的治疗靶点仍然未知。随着基因高通量测序分析的出现,在临床样本和实验模型中发现了多种急性缺血性脑卒中后大脑和外周血中异常表达的非编码RNA。脑卒中后大脑中差异表达的非编码RNA在病理过程中发挥着至关重要的作用,导致神经保护或恶化,因此非编码RNA可以作为急性缺血性脑卒中的治疗靶点。此外,外周血中不同表达的非编码RNA也可能成为急性缺血性脑卒中预测、诊断和预后的生物标志物。特别是,外周免疫细胞中的这些非编码RNA最近被证明参与了急性缺血性脑卒中后的外周和大脑免疫反应。此次综述总结了非编码RNA(微小RNA、长链非编码RNA和环状RNA)在急性缺血性脑卒中诱导的脑损伤的病理过程中的作用,以及这些非编码RNA作为急性缺血性脑卒中预测、诊断和预后的生物标志物的功能的最新进展,从而为非编码RNA在急性缺血性脑卒中中的相关临床应用提供新的思路。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4324-8009 (Qiwen Deng); https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2196-3995 (Fuling Yan)