NRR:江西省人民医院徐仁伵团队揭示与炎症相关的OSMR潜在基因与散发性和C9orf72相关肌萎缩侧索硬化中的作用
撰文:陈文志,徐仁伵
近年来,肌萎缩侧索硬化作为一种神经退行性疾病,其发病机制至今尚未完全阐明,但炎症反应在其发病过程中扮演着重要角色[1]。无论是在散发性肌萎缩侧索硬化还是C9orf72相关的肌萎缩侧索硬化中,炎症因子的异常表达和异常激活被认为与神经元损伤及死亡密切相关[2, 3]。小胶质细胞作为中枢神经系统中的免疫细胞,具有调节神经炎症反应和清除细胞碎片的重要作用。活化的小胶质细胞分为促炎症型M1和抗炎症型M2两种,其中M1型小胶质细胞促进炎症反应,而M2型小胶质细胞则具有抗炎和神经保护作用[4]。然而,散发性肌萎缩侧索硬化和C9orf72相关的肌萎缩侧索硬化患者的小胶质细胞活化状态及其与炎症反应的关系尚未充分阐明。在此背景下,能否通过分析散发性肌萎缩侧索硬化和C9orf72相关的肌萎缩侧索硬化患者脑组织样本,探索是否存在影响炎症反应的潜在驱动基因?进而为其治疗提供新的思路和靶点?
为解决以上问题,来自中国江西省人民医院徐仁伵团队在《中国神经再生研究(英文版)》(Neural Regeneration Research)上发表了题为“OSMR is a potential driver of inflammation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis”的研究。该研究通过基于可扩展算法的精确细胞网络重建方法(SJARACNe)网络驱动基因分析工具NetBID2.0对散发性肌萎缩侧索硬化和C9orf72相关的肌萎缩侧索硬化患者的测序数据进行分析,发现OSMR(oncostatin m receptor)基因可在肌萎缩侧索硬化发挥关键作用,可能通过介导神经炎症反应参与其发展。此外,研究还发现散发性肌萎缩侧索硬化和C9orf72相关的肌萎缩侧索硬化患者中OSMR的活性和表达存在差异,这暗示OSMR可能成为潜在的诊断和预后标志物。
徐仁伵等首先进行了样本聚类分析,将不同的脑组织样本进行分类。然后,分别针对小脑和额叶皮质进行驱动基因推断,并通过比较这2种脑组织中的驱动基因,分析其差异。接着筛选出与肌萎缩侧索硬化相关的显著差异表达基因,并对其进行功能富集分析,以了解这些基因的生物学功能。此外还对特定基因的表达和活性进行了详细分析,以揭示其在不同样本亚型中的变化。聚类分析结果显示,不同脑组织样本存在显著差异,因此只能分别进行驱动基因推断。在小脑和额叶皮质中,分别鉴定出了头部30种驱动基因。这些驱动基因中,有一些与乳腺癌亚型、肺肌肉肉瘤等疾病相关(图1)。
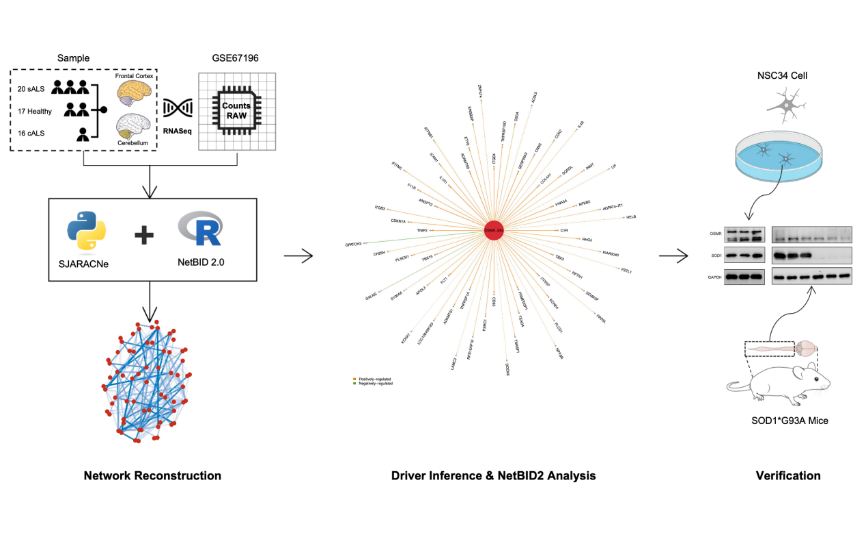
图1 对脑组织测序数据集进行的基于SJARACNe网络的NetBID2.0分析表明,OSMR是一个与炎症相关的潜在驱动基因,与肌萎缩性脊髓侧索硬化的发病机制有关联(图源:Chen et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
通过网络构建和功能富集分析,发现OSMR是一个显著的驱动基因。在与健康对照组比较时,肌萎缩侧索硬化患者中OSMR的表达和活性均显著增加。此外,OSMR与炎症反应相关的靶基因中,有多个基因与其紧密相关,这进一步表明,OSMR在肌萎缩侧索硬化的炎症调控中具有重要作用(图2)。

图2 头部显著差异活动驱动因子及其靶基因的生物学功能(图源:Chen et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
此外,OSMR不仅在健康对照组和肌萎缩侧索硬化组之间存在差异,且在散发性肌萎缩侧索硬化和C9orf72相关的肌萎缩侧索硬化的亚组之间也存在差异(图3)。

图3 OSMR的重要性及其在不同亚群中的表达模式,以及OSMR靶基因的功能和网络特征(图源:Chen et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
通过在细胞和小鼠模型中进行Western blot验证发现,与对照组相比,肌萎缩侧索硬化模型中OSMR的表达显著升高。这与之前基因推断的分析结果一致,进一步证实OSMR在肌萎缩侧索硬化中的关键作用(图4)。

图4 OSMR在肌萎缩侧索硬化细胞和小鼠模型中高度表达(图源:Chen et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
通过综合运用SJARACNe和NetBID2.0等工具揭示肌萎缩侧索硬化发病机制中潜在的关键驱动基因OSMR及其在调控炎症反应中的重要作用,研究OSMR的生理和病理效应有助于更好地理解神经退行性疾病的机制,并为这些疾病的治疗提供新的启示。尽管该研究取得了一些重要发现,但仍存在一些限制条件。比如由于技术和经费等限制,暂时无法验证C9orf72相关的肌萎缩侧索硬化模型中OSMR活性和表达水平是否高于散发性肌萎缩侧索硬化。此外,OSMR在肌萎缩侧索硬化中的炎症机制尚未得到验证。总之,该研究为揭示肌萎缩侧索硬化发病机制中的关键驱动因素提供了重要线索,尽管还有许多不确定性和未验证的假设,但未来仍然有希望通过深入的实验和临床研究,进一步探索OSMR在肌萎缩侧索硬化中的作用及其在疾病治疗中的潜力。
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.391309
参考文献
[1] Van Es MA, Hardiman O, Chio A, et al. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Lancet. 2017;390(10107):2084-2098.
[2] Feldman EL, Goutman SA, Petri S, et al. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Lancet. 2022;400(10360):1363-1380.
[3] Giallongo S, Longhitano L, Denaro S, et al. The role of epigenetics in neuroinflammatory-driven diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(23):15218.
[4] Lall D, Baloh RH. Microglia and C9orf72 in neuroinflammation and ALS and frontotemporal dementia. J Clin Invest. 2017;127(9):3250-3258.

通讯作者:徐仁伵,教授,主任医师,博士生导师,德国乌尔姆大学、美国路易威尔大学博士后。江西省医学会神经病学分会主任委员、中华医学会神经病学分会委员、中国老年医学学会神经科学分会常委兼锥体外系组长、中国医师协会神经内科医师分会委员。已获得6项国家自然科学基金项目资助。长期从事帕金森病、肌萎缩侧索硬化的临床和实验研究。至今发表学术论文300多篇,其中英文SCI收录70余篇。




